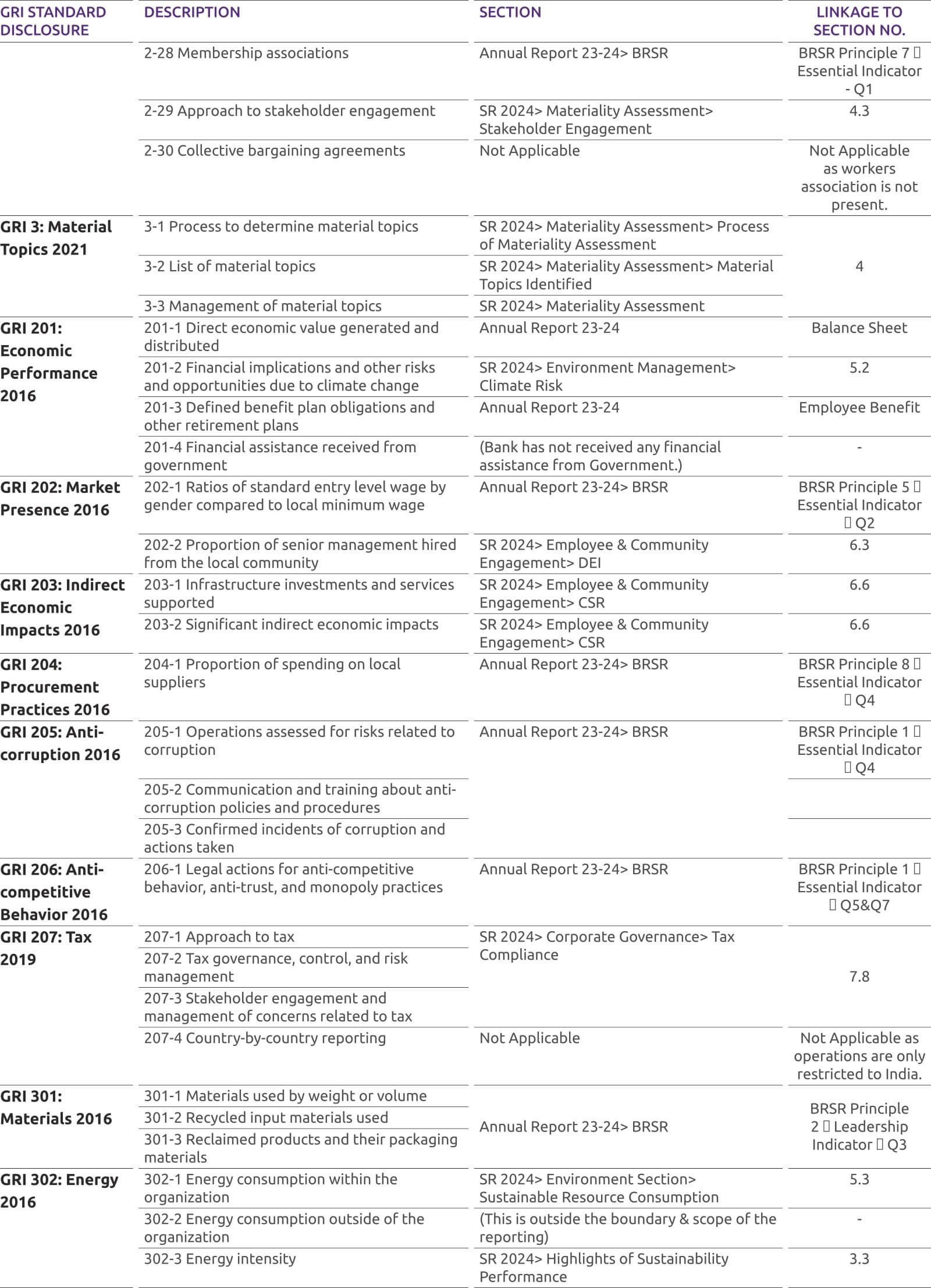
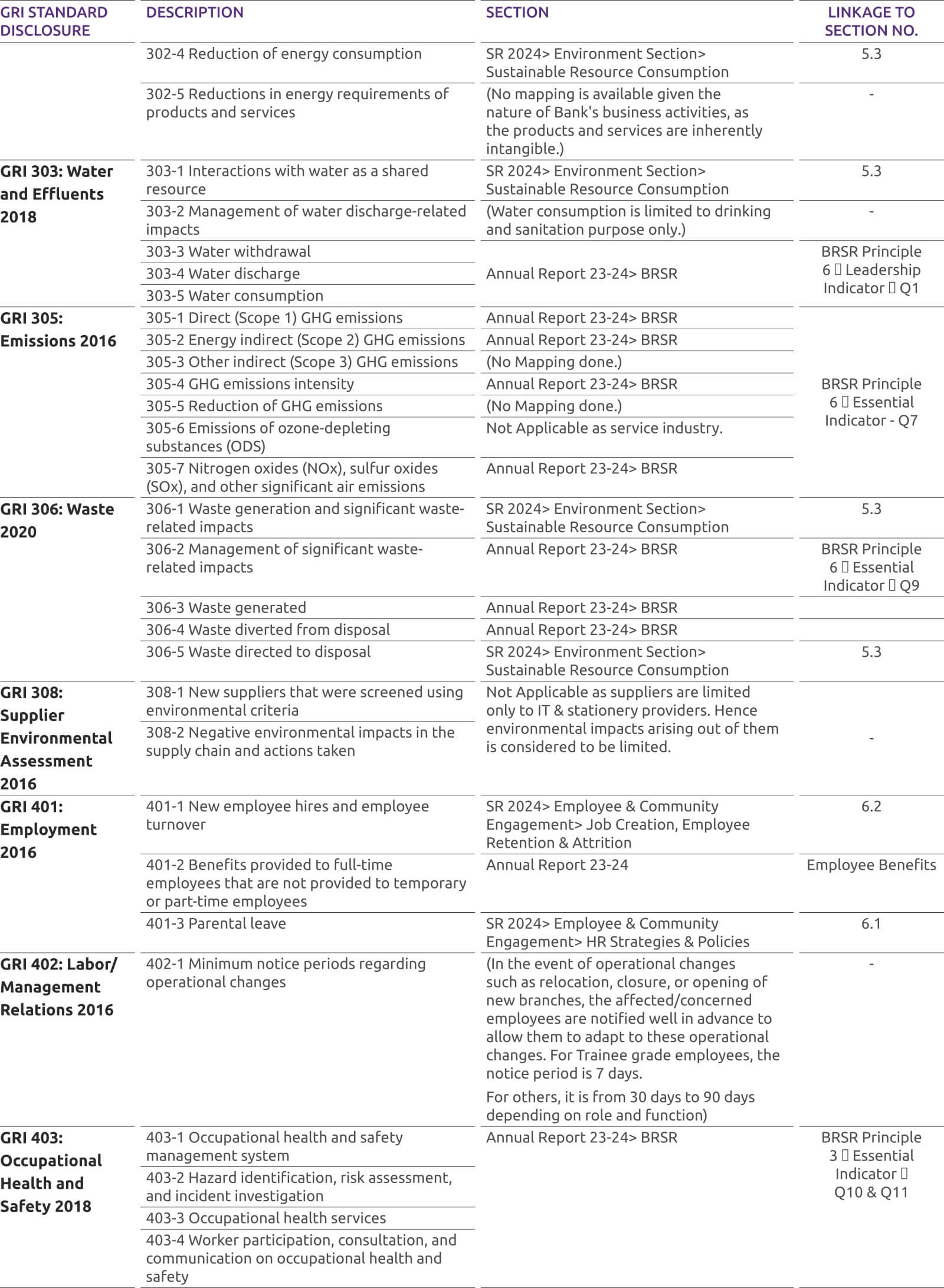
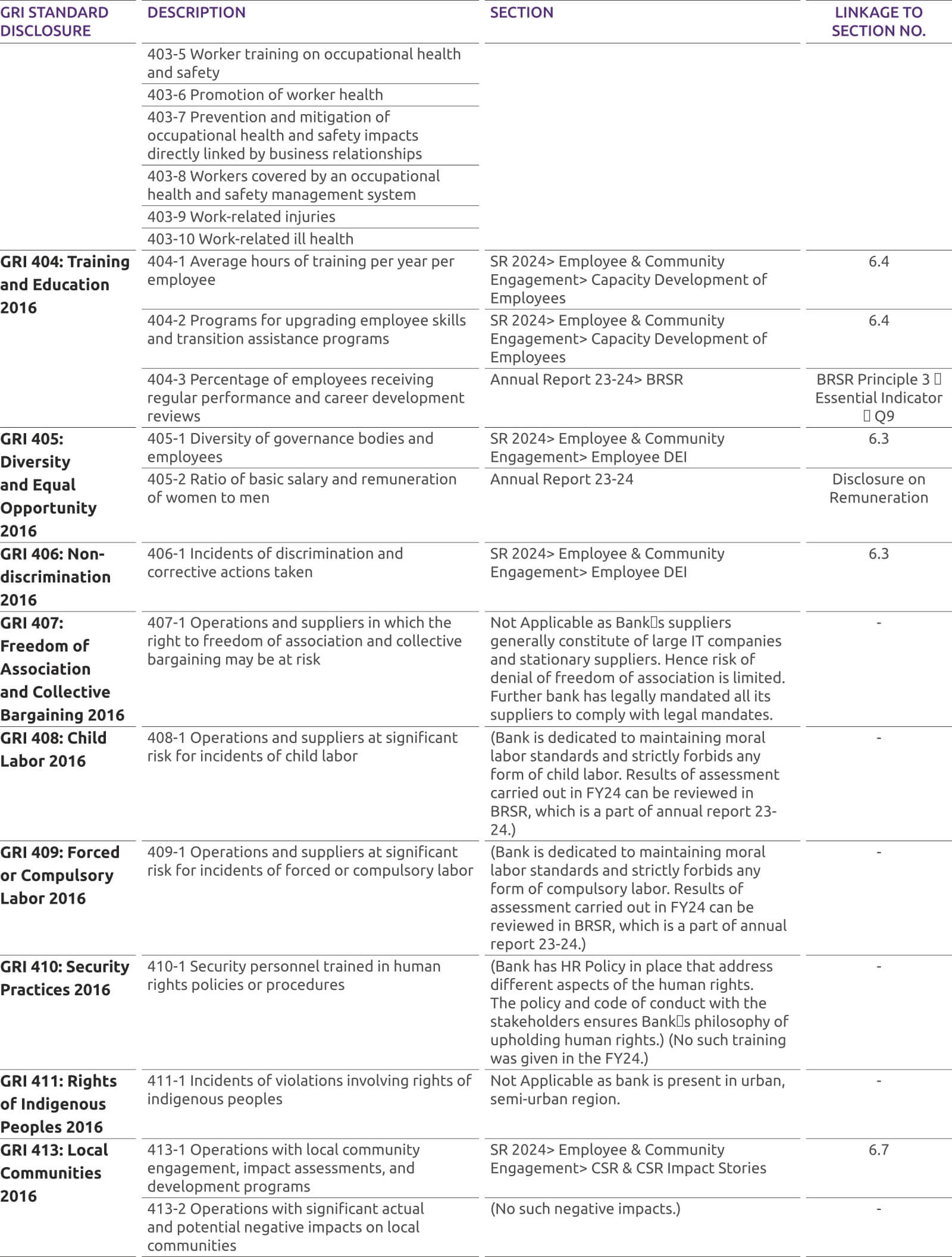
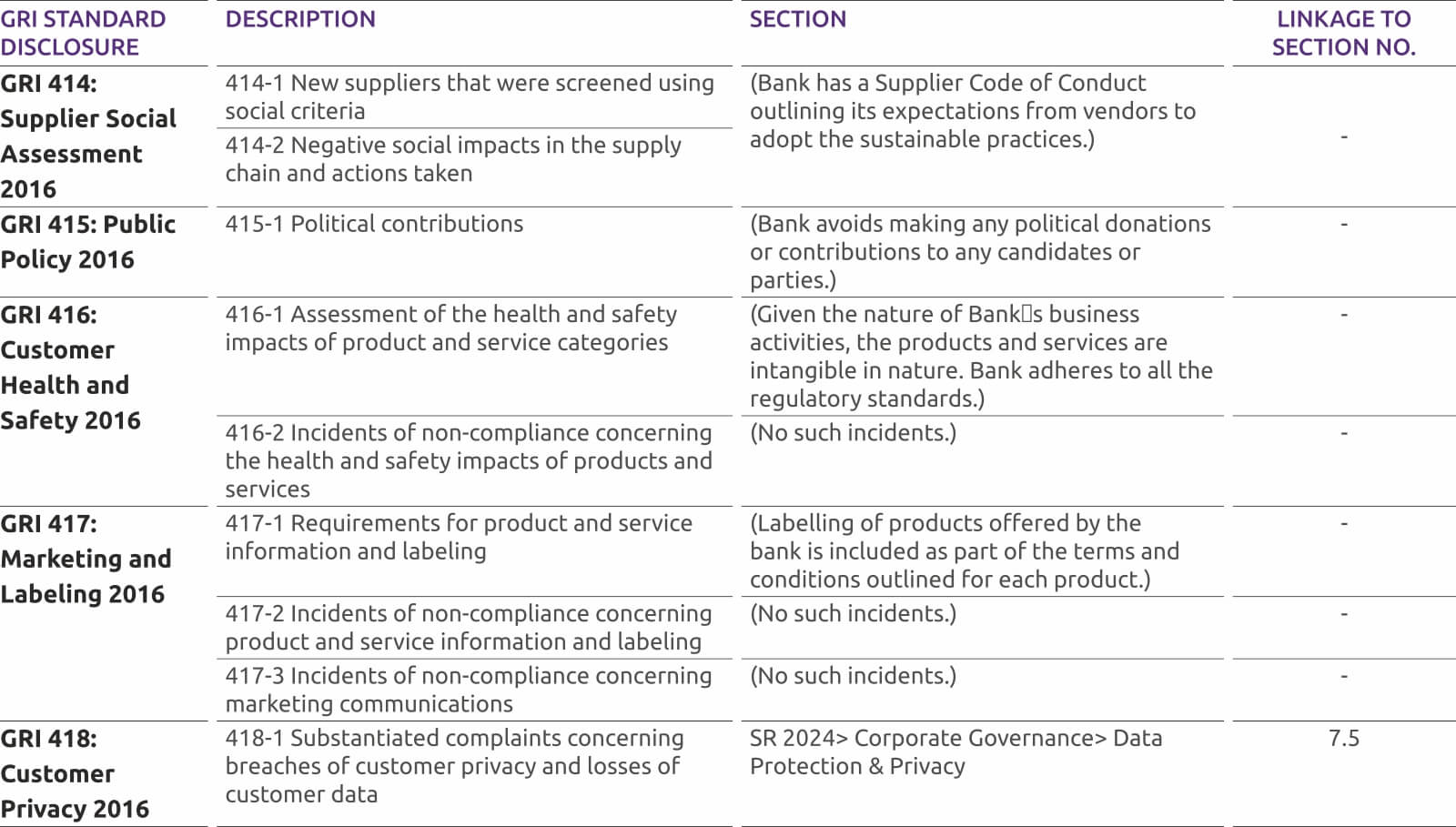
-
-
COVID-19 Precautionary Steps
Considering COVID-19 we have taken precautionary steps demanded by the situation. Our branches will be open, with required hygiene measures and reduced staff.
-
Revision in Savings Account Interest Rates
Revision in Savings Account Interest rates effective April 01, 2022
-
Customer Compensation and Protection Policy limiting the liability of customers in unauthorized electronic transactions is available under Bank Policies section for perusal of customers.
-
Our Avinashi branch located at The Utkarsh BANK Ltd. Shop No 5/215 Rajan Nagar Opp to weekly Market, K K Pudur post Avinashi Taluk, Tirupur - 641654, will be closed w.e.f April 30, 2022. It is being merged with our Tirupur branch.
-
Menu
Notifications
-
COVID-19 Precautionary Steps
Considering COVID-19 we have taken precautionary steps demanded by the situation. Our branches will be open, with required hygiene measures and reduced staff.
-
Revision in Savings Account Interest Rates
Revision in Savings Account Interest rates effective April 01, 2022
-
Customer Compensation and Protection Policy limiting the liability of customers in unauthorized electronic transactions is available under Bank Policies section for perusal of customers.
-
Our Avinashi branch located at The Utkarsh BANK Ltd. Shop No 5/215 Rajan Nagar Opp to weekly Market, K K Pudur post Avinashi Taluk, Tirupur - 641654, will be closed w.e.f April 30, 2022. It is being merged with our Tirupur branch.
U-Sustain
USFBL Sustainability Report FY 2023-24
- Message from Chairman
- Message from CEO
- Megatrends Shaping Future
Message From Chairman

Considering recent developments that highlight the need for sustainable business
practices, we remain steadfast in upholding transparency and accountability throughout our sustainability journey,
which we envision to be perpetual.
Dear Stakeholders,
We at Utkarsh Small Finance Bank are delighted to present you with our first Sustainability
Report. The Bank that began with a goal to serve the unserved and the underserved communities financially,
is now taking a larger role towards its commitment towards ESG, holistically.
The world is facing several
pressing issues that underscore the importance of adopting sustainable practices. Climate change is causing
more frequent and severe weather events, impacting agriculture, infrastructure, and communities worldwide. Additionally,
plastic pollution is damaging ecosystems and harming wildlife, while deforestation is contributing to biodiversity loss
and altering natural habitats. These challenges highlight the urgent need for global sustainability efforts to protect
our environment, support resilient communities, and ensure a stable future. Adopting sustainable practices is now
more critical than ever to mitigate these impacts and promote long-term well-being for the global community.
India, at
the 26th session of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP 26) in November 2021, announced its
target to achieve net zero by 2070. Utkarsh Small Finance Bank is deeply inspired by the global movement and is desirous
of playing its part towards our nation’s commitment,therefore it has taken its initiatives fostering sustainability as an
important component of its business model.
Sincerely,
Parveen Kumar Gupta
Chairman
Utkarsh small Finance Bank Limited
Message from MD & CEO

Our steps in paperless and digital banking are representative of bank’s endeavors towards sustainability
and being climate friendly. It will also contribute to increase the operational efficiency of the bank.
Dear Stakeholders,
I am delighted to present the first Sustainability Report of Utkarsh Small Finance Bank. A commitment of our Bank
towards environment, sustainability and governance, aligned with internationally recognised GRI standards. Aligning business goals
with Sustainability will be the norm in the coming days.
Utkarsh Small Finance Bank is focusing on climate resilience through a holistic
approach. Expanding and strengthening our presence across the nation requires awareness of the impact on the bank and environment,
focusing on businesses we service and their associated Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) impact.
Utkarsh Small Finance Bank has
achieved the prestigious GRIHA 5-star certification, making it one of few buildings in Uttar Pradesh to achieve this. Utkarsh was
conferred upon this award and certification for designing, constructing, and operating high-performance green buildings that minimize
resource consumption, waste generation, and ecological impact within national standards. Women empowerment has always been a core aspiration
and objective at USFBL. The Women managers led branches are one of the finest examples of this. With more than 30 lakh women customers and
beneficiaries, the bank is significantly putting its focused endeavors towards their empowerment and social well-being. In order to achieve
our vision of being a trusted financial service provider, the bank realizes the need to address these ESG risks & impacts in a structured manner
and take measures at the appropriate stage.
Aiming to continually excel as a responsible enterprise, this report demonstrates our dedication to promoting the ESG principles and fostering sustainability as a crucial part of the business model. Our steps in paperless and digital banking are representative of bank’s endeavors towards sustainability and being climate friendly. It will also contribute to increase the operational efficiency of the bank. At Utkarsh Small Finance Bank, we uphold our tagline ‘Aapki Ummeed Ka Khaata’ by not only valuing the trust and confidence of our customers, but also by integrating sustainability and ESG practices into our core operations, ensuring that we safeguard the future while delivering reliable and dependable banking services. Through the incorporation of ESG principles into our financial endeavors, we aspire to make a modest yet meaningful contribution towards advancing the global initiatives aimed at fulfilling the UN SDGs, while simultaneously generating longlasting value for our business. We recognize that sustainability goes beyond mere business considerations, and we are committed to achieve a balance between business expansion and sustainability. Sustainability isn’t merely an objective for us; it’s a continuous path that we are fully committed to. We deeply appreciate your ongoing support and confidence in Utkarsh Small Finance Bank.
Moving forward, Together
Sincerely,
Govind Singh
Managing Director & CEO
Utkarsh Small Finance Bank Limited
Megatrends Shaping The Future
The future of ESG in banking sector is being shaped by multiple internal & external stressors. The World Economic Forum's Risk Report for 2024 reveals a significant shift in global risks over a 10-year period, highlighting emerging trends and persistent challenges. A trend analysis of the data illustrates the evolving landscape of risks and their implications for various aspects of society.

Starting with the environmental category, it's evident that concerns related to climate change, extreme
weather events, and biodiversity loss remain consistent over the years. However, there is a notable escalation in the
severity of these risks by 2024, as indicated by the introduction of "Critical change to Earth systems" and "Biodiversity loss
and ecosystem collapse" in 2024. This suggests a heightened awareness of environmental degradation and its potential catastrophic
consequences. Bank is in cognizance of these issues & has adopted ESG policy, which is committed towards sustainable resource consumption
& energy efficiency in general.
In the socioeconomic sphere, there is a noticeable progression from issues like social cohesion erosion and
livelihood crises towards larger-scale involuntary migration and natural resource shortages. This shift reflects the deepening
impact of socioeconomic disparities and resource constraints on global stability and human well-being. Bank has been focusing
on job creation by direct & indirect means at national level and livelihood improvement of MFI customers.
The rise of
technological risks, such as cyber insecurity and adverse outcomes of AI technologies, underscores the growing influence of
technology on various aspects of society. These risks highlight the need for robust cybersecurity measures and ethical frameworks
to mitigate potential harms associated with technological advancements.Additionally, the emergence of societal risks like
polarization and misinformation reflects growing social divisions and challenges to democratic norms. These risks have the potential
to exacerbate existing tensions and undermine social cohesion, posing significant threats to governance and stability.
Overall, the trend analysis reveals a convergence of environmental, socioeconomic, technological, and societal risks, signaling the
interconnected nature of global challenges. Addressing these risks will require coordinated efforts across sectors and international
cooperation to build resilience and foster sustainable development in an increasingly complex and uncertain world.

Small Finance Banks Landscape in 2024
SFBs were set up in 2016 to meet the financial needs of the marginalised sections of society. They are differentiated or niche banks with minimum net worth of 200 crore, lower than other SCBs. At end-June 2023, twelve SFBs with 6,589 domestic branches across the country were operational. The geographical concentration of SFBs – measured by the Herfindahl- Hirschman Index (HHI) – has been coming down in terms of both number of reporting offices as well as credit and deposits. This indicates progressive diversification and increasing outreach of SFBs in line with their mandate of serving the marginalised sections

SFBs serve a critical role in delivering credit to under-banked segments. Some entities, which were NBFC-MFIs earlier and subsequently converted to SFBs, retained their earlier business models. Consequently, the share of unseured lending in their portfolios, especially to microfinance and joint liability group (JLG) borrowers, is high.
RBI’s report on ‘Trend & Progress of Banking in India 2022-23’ suggests that the lack of asset diversification is often coupled with geographical concentration, implying significant concentration risk.
Bank is spread across 26 states & UTs in India, implying relatively less concentration risk.
Opportunities and Challenges of New Technology Adoption
The adoption of new technologies enables neo-banks and non-banks to generate additional revenue, reduce expenses, and better manage risk exposure. It allows banks to provide more convenient and personalized services to their customers, while also enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of banking operations. However, this technological advancement has also led to an increase in fraud and data breach risks. To safeguard the system, concerted efforts are required from all stakeholders, including regulators, banks, and customers. Reserve Bank of India has been proactive in updating regulations to protect customers without stifling innovation.
Technology has created a more inclusive and efficient financial ecosystem, with Indian banks increasingly leveraging it to improve customer experience and address last-mile issues. Nonetheless, the adoption of new technology has heightened the risks of cyber-attacks, data breaches, and operational failures. Moving forward, banks must better recognize and address these technologies and cyber security risks to minimize potential vulnerabilities. The evolving nature of risks in the banking system calls for building resilience through good governance and robust risk management practices.
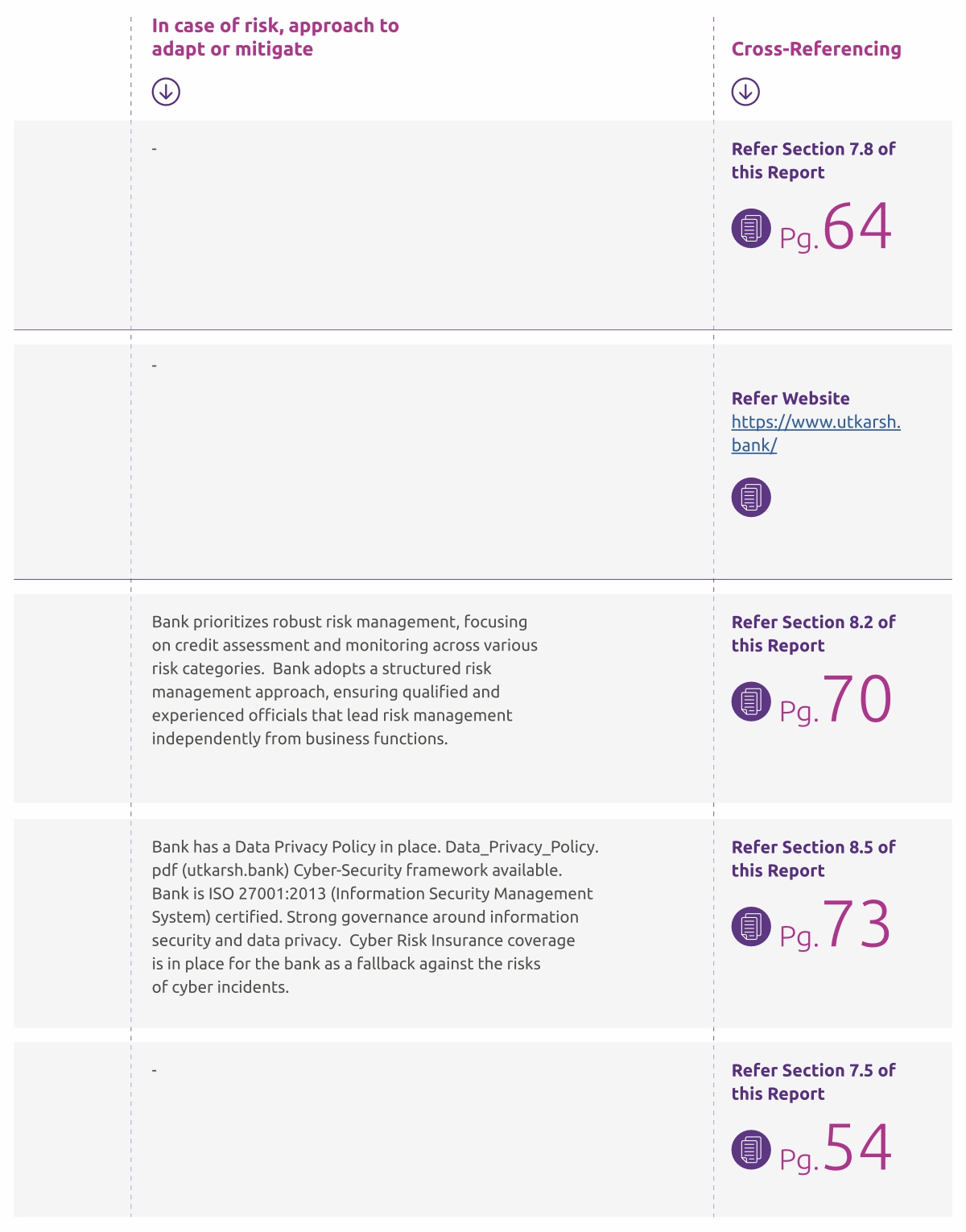
To cater to the challenges of adoption of new technology such as cyberattacks, data breaches etc., Bank has a robust cyber-security and data protection & privacy framework (Refer to Section 8.5 of this report) in place.

Green Initiatives
With climate change being recognised as the most critical challenge, the Reserve Bank has been playing a key role in nudging banks towards mobilising green resources for green activities and projects.
Acceptance of Green Deposits
Reserve Bank of India issued a framework for acceptance of green deposits on April 11, 2023 to encourage REs to offer green deposits to customers, protect depositors’ interest, address greenwashing risks and help augment the flow of credit to green activities/ projects.

The allocation of funds raised through green deposits will also be subject to annual independent third-party verification/assurance. This would not, however, absolve the RE of its responsibility regarding the end-use of funds, for which internal checks and balances will have to be followed.
Adoption of Artificial
Intelligence in Indian Banks
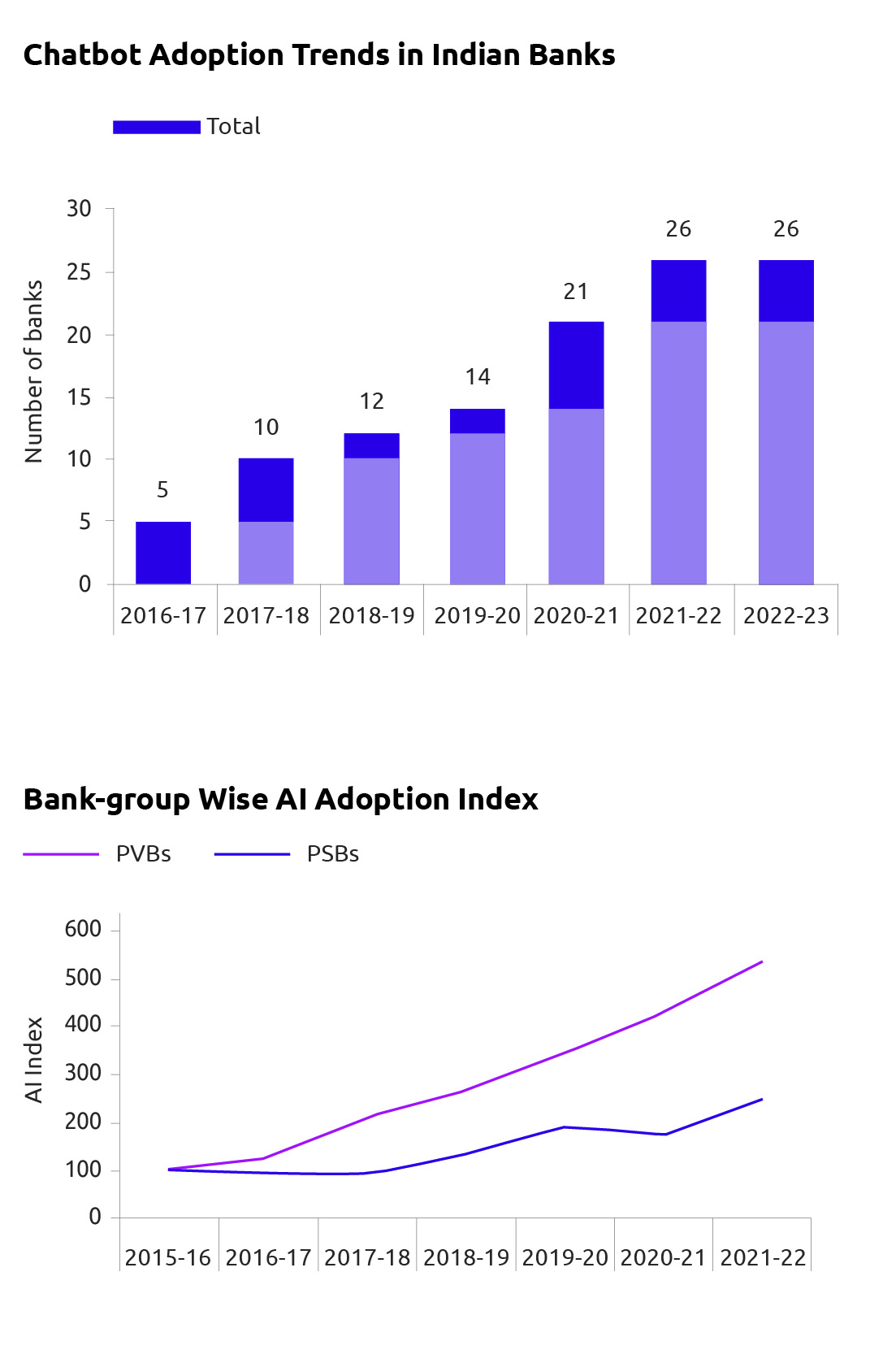
Globally, banking and financial services are leading the adoption of AI (McKinsey, 2017). One of the prominent usages of AI across service industries is chatbots that can converse — either through text or through voice — with human users in natural languages. To measure AI awareness and potential adoption by Indian banks, a textual analysis is performed on the annual reports of Indian banks from 2015-16 to 2021-22, using a combination of related keyword matching and named entity recognition approaches while leveraging popular dictionaries/glossaries related to AI and ML. The survey shows that at end June-2023, 11 out of 12 PSBs and 15 out of 21 PVBs already had some form of chatbot and virtual assistant by using AI and ML technologies (Shown in Figure 2). In most of the cases, the chatbots are accessible through the banks’ websites. In case of PSBs, mega mergers seem to have given a boost to adoption of chatbots, with merged entities adopting the technology of acquirers (Shown in Figure 3). NBFCs are also introducing chatbots for customer services.
About the Report
Reporting Frameworks and Cycle
This is the first annual Sustainability Report developed in line with the Global Reporting Initiative framework – Sustainability Reporting Standards. It covers the period from 1st April 2023 to 31st March 2024, unless otherwise specified, and includes all businesses under our operational control. This report is an attempt to explain the sustainability strategy and performance of the bank to all the stakeholders. In adherence to GRI reporting principles, the report addresses sustainability issues relevant to both, stakeholders and business operations of the bank.
Reporting Scope and Boundary
The scope and boundary of operations include 888 branches (which includes offices and branches), 320 ATMs & 619 Micro ATMs across 26 sttes in India. Bank do not have any subsidiary or associate company. Hence, the reporting scope and the boundary relevant to the present sustainability report are applicable to an individual entity with no subsidiaries.
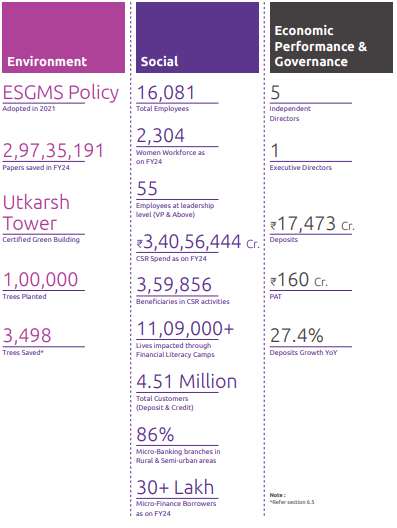
Highlights of Sustainability Performance
- Process of Materiality Assessment
- Materiality Matrix
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Emerging ESG Risks & Opportunities
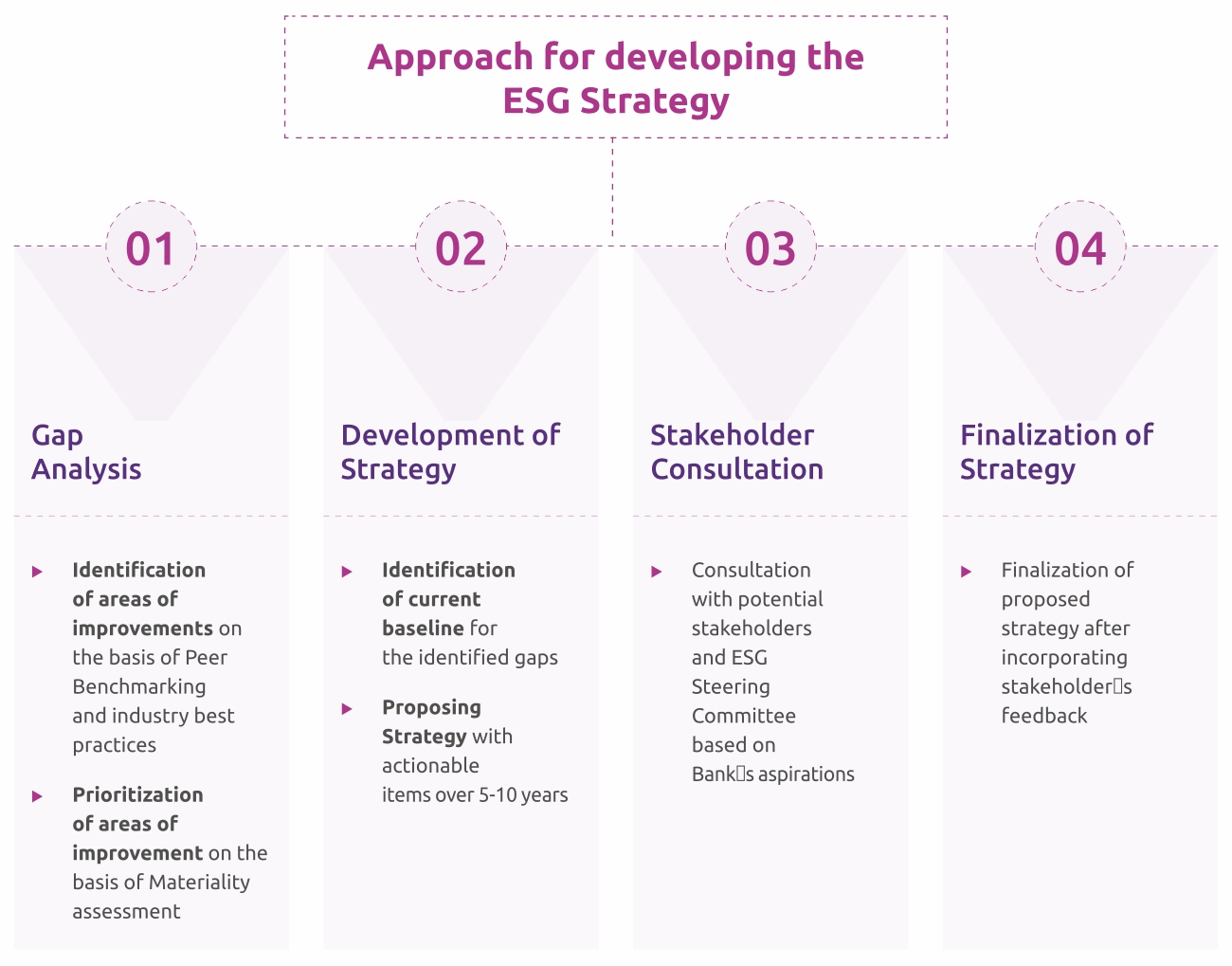
Materiality Assessment
Process of Materiality Assessment
Materiality Assessment is an exercise through which an organization identifies the most impactful sustainability topics and set its priorities. The process of materiality assessment is given in below.
Identification of relevant ESG themes- 32 relevant Environmental, Social & Governance-related topics were
identified from (i) peer analysis, (ii) industry best practices and (iii) analysis of industry standards like GRI and SASB
A preliminary survey was conducted of these topics with 26 senior - most management team members.The objective of the
survey was to identify critical and relevant topics that may be included in the materiality analysis survey.
Capacity
Building Workshop - A workshop was conducted on 8 May 2024 with 28 senior management members, which included Mr. Govind Singh
(MD & CEO), Mr. Sarju Simaria (CFO), Mr. Hitain Sharma (CHRO), Mr. Alok Pathak (CRO) and Mr. Mukesh Singh Verma (CCO), amongst others.
The objective of the workshop was (i) to discuss the relevant topics vis-à-vis the result of the preliminary survey, (ii) identify the
material stakeholders, and (iii) gather their support for the final materiality analysis. The workshop resulted in identification of 18
relevant topics and key material stakeholders.
Identification of Material Topics- The outcome of the capacity building workshop was 18 (out of 32) identified material issues for Bank, which are mentioned below:

Stakeholder Survey - Once relevan topics were identified, and a list of internal and external stakeholder was gathered; a materiality
survey was started. A diverse set of internal and external stakeholders were engaged in this process.
An online survey tool was deployed for capturing feedback
from all relevant stakeholders. For the survey, a scale of 1-5 was adopted, where respondents rate each topic from 1 (less significant) to 5 (most significant).
Compiling results & identifying material topics - After data collection, the survey results were analyzed using statistical methods to understand the top priority topics for Bank. Accordingly, Materiality Matrix is made, which showcases significance of identified material issues for the bank.
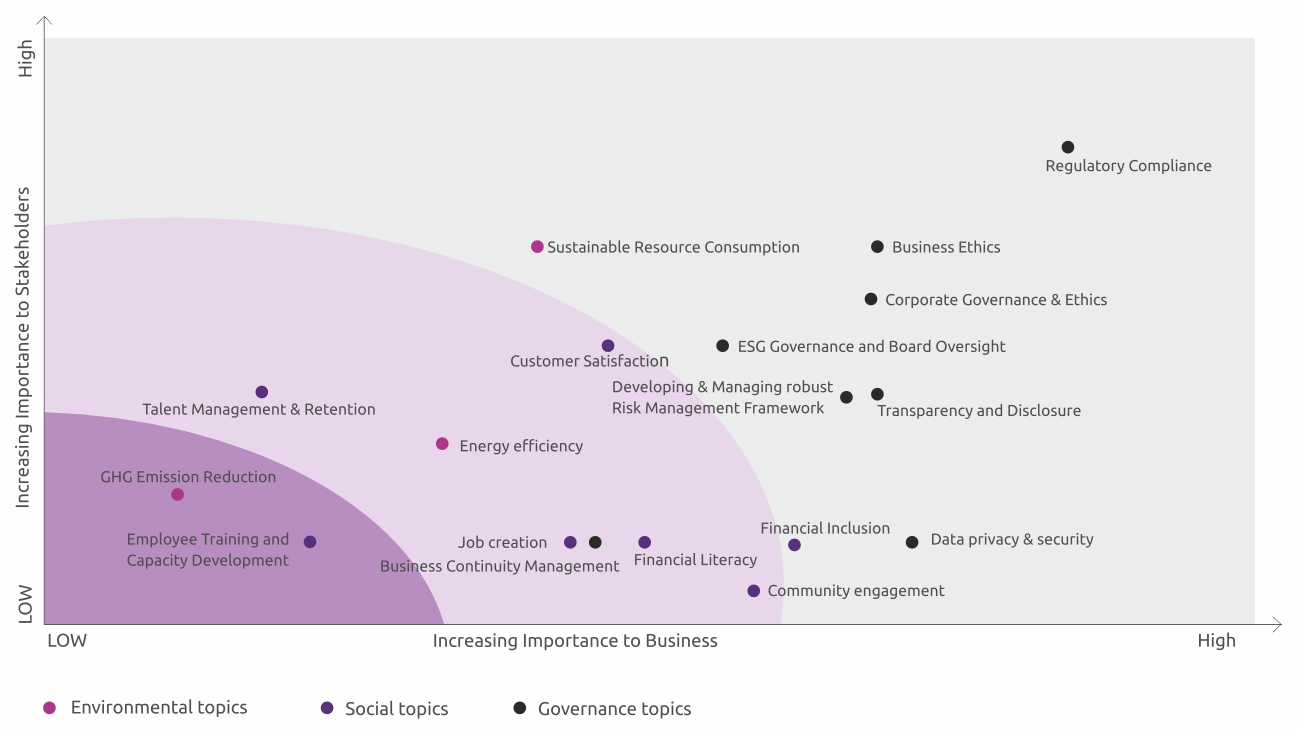
Materiality Matrix
The X-axis of the materiality assessment graph implies importance to business whereas the Y-axis implies importance to the Bank’s stakeholders. Top-right hand corners
depicts the most significant and the bottom left-hand corner has the least significant topics identified by internal & external stakeholders.
Out of 18 relevant topics, 10 has been
identified as highly significant, 6 moderate & 2 have been identified as less significant topics. These are in line with trends observed in cases of peers; where stakeholders have been
seen emphasizing governance topics over social and environmental topics.
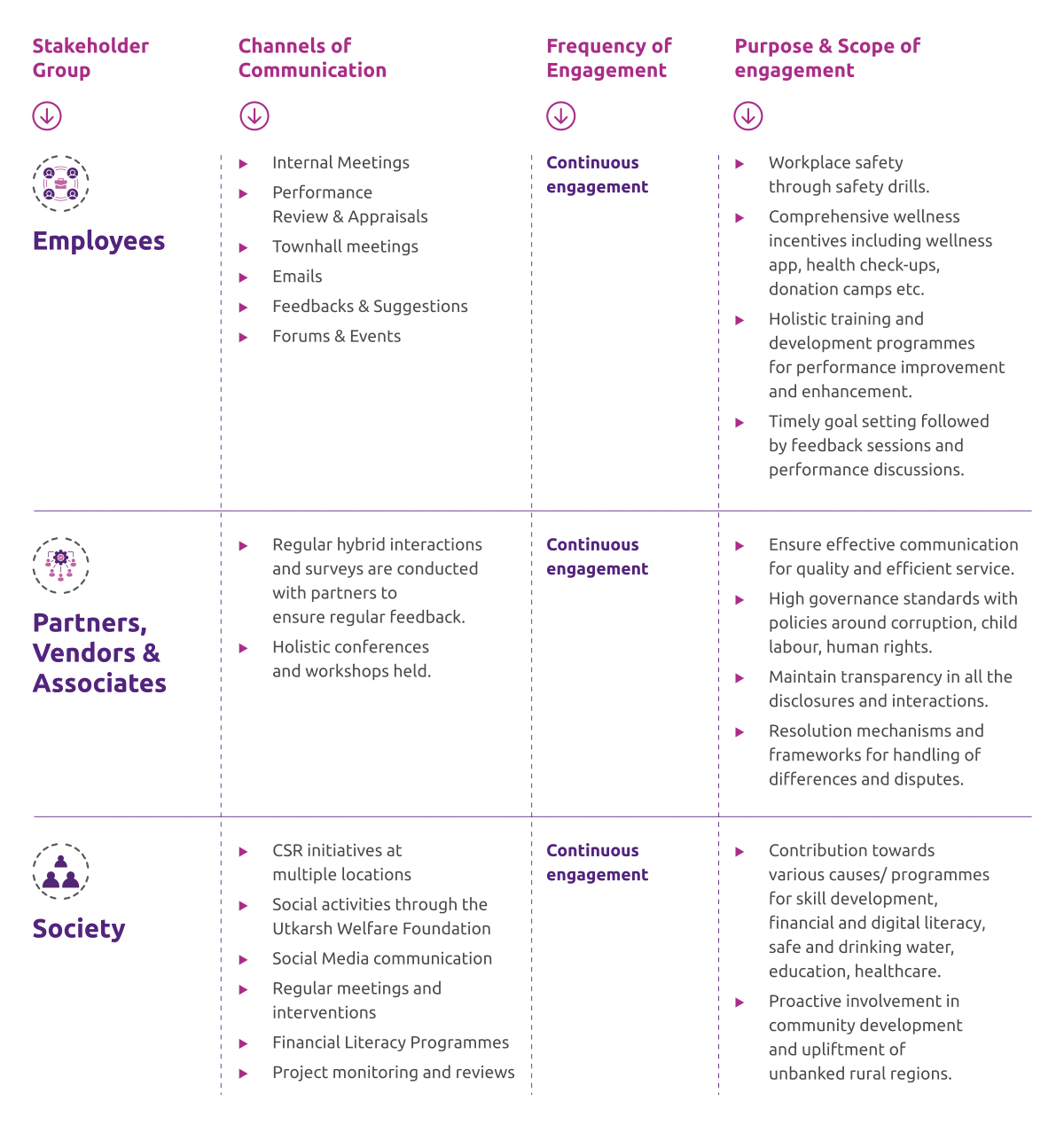
Stakeholder Engagement
Bank prioritizes transparent and open communication and engagement with its stakeholders. The valuable feedback from these stakeholders is crucial in enhancing the bank’s business strategies and risk management practices. This feedback enables the bank to refine its internal processes, capitalize on business opportunities, reduce operational uncertainties, and maintain a competitive edge, all while delivering value to every stakeholder involved.
Emerging ESG Risks & Opportunities
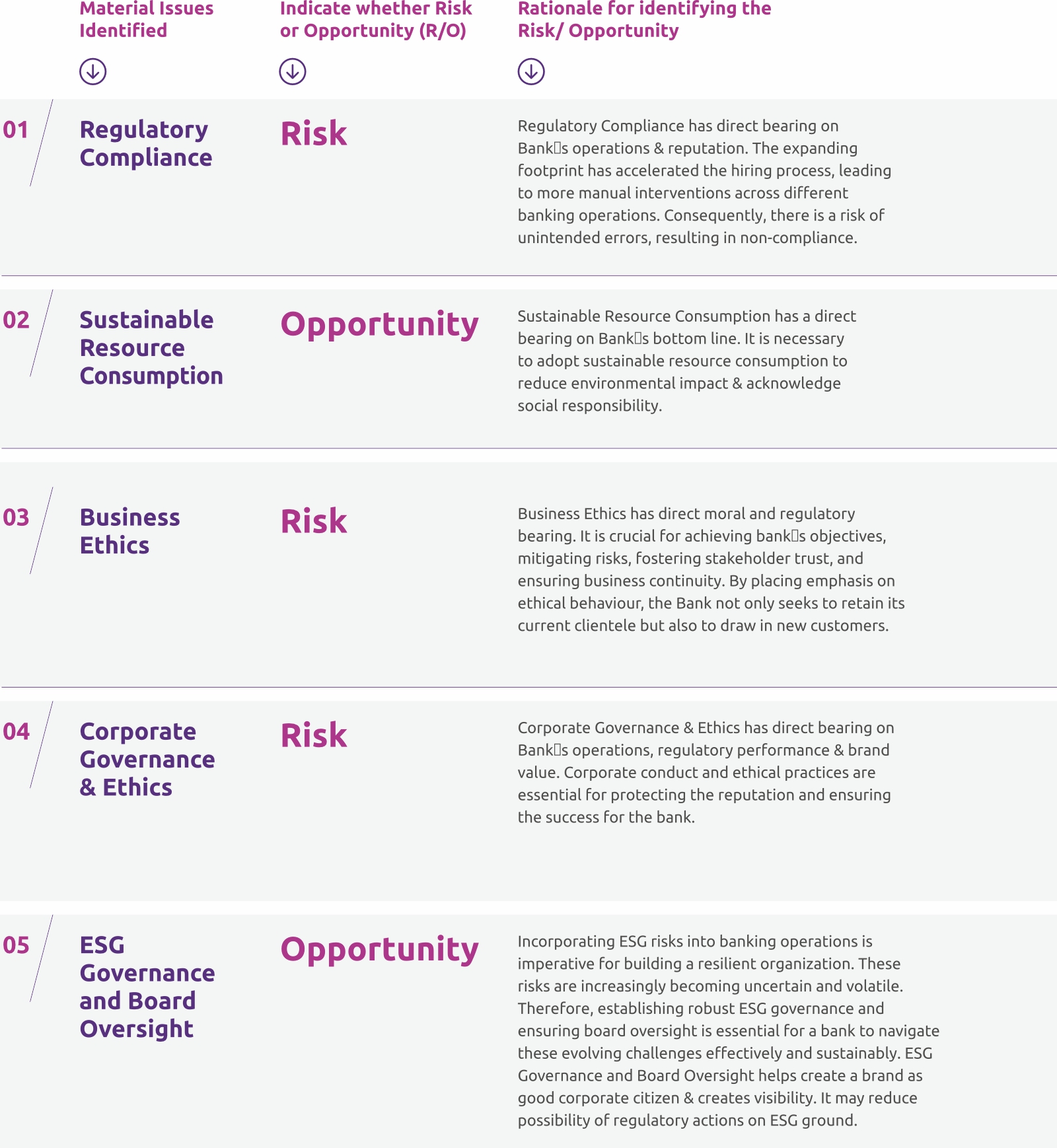
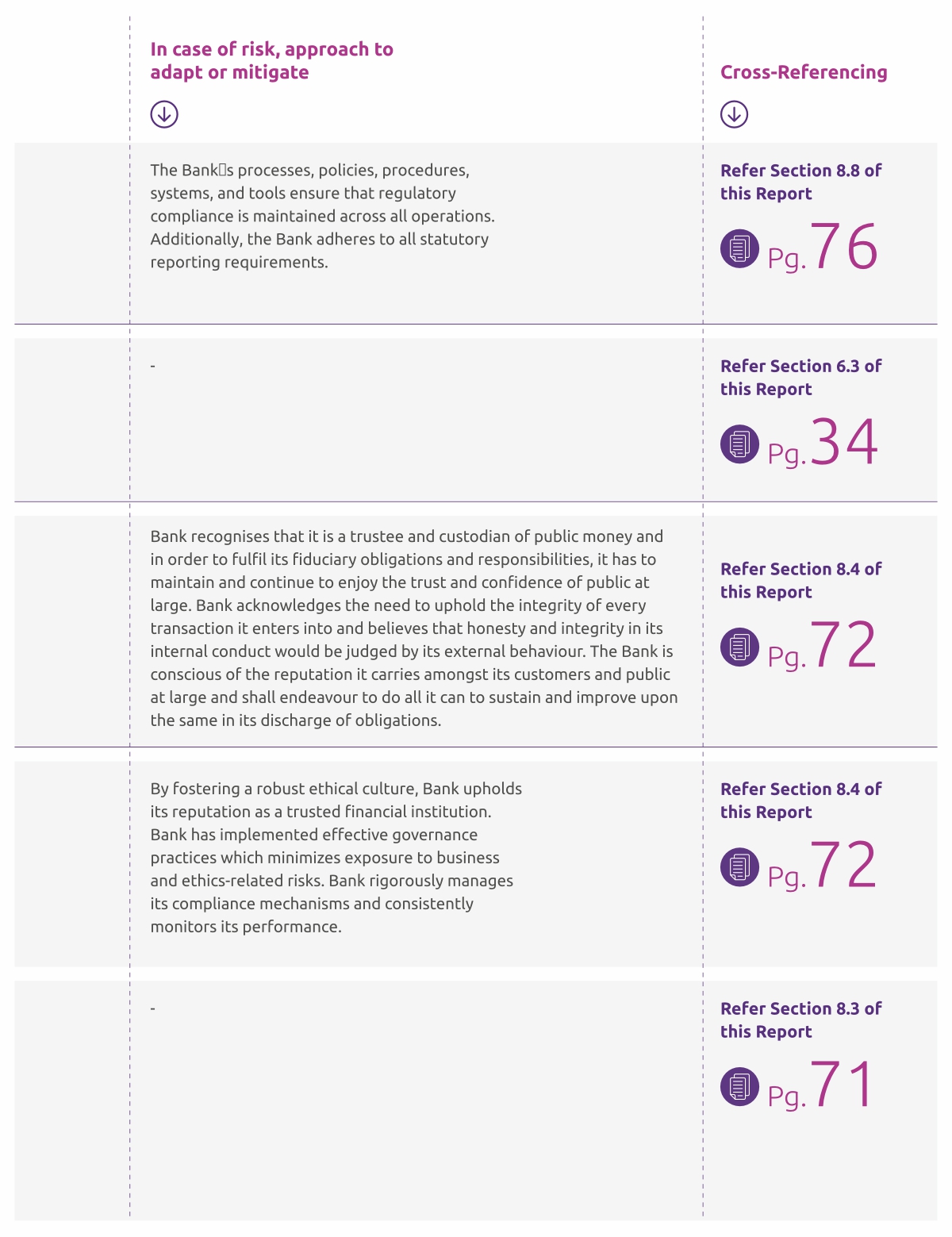
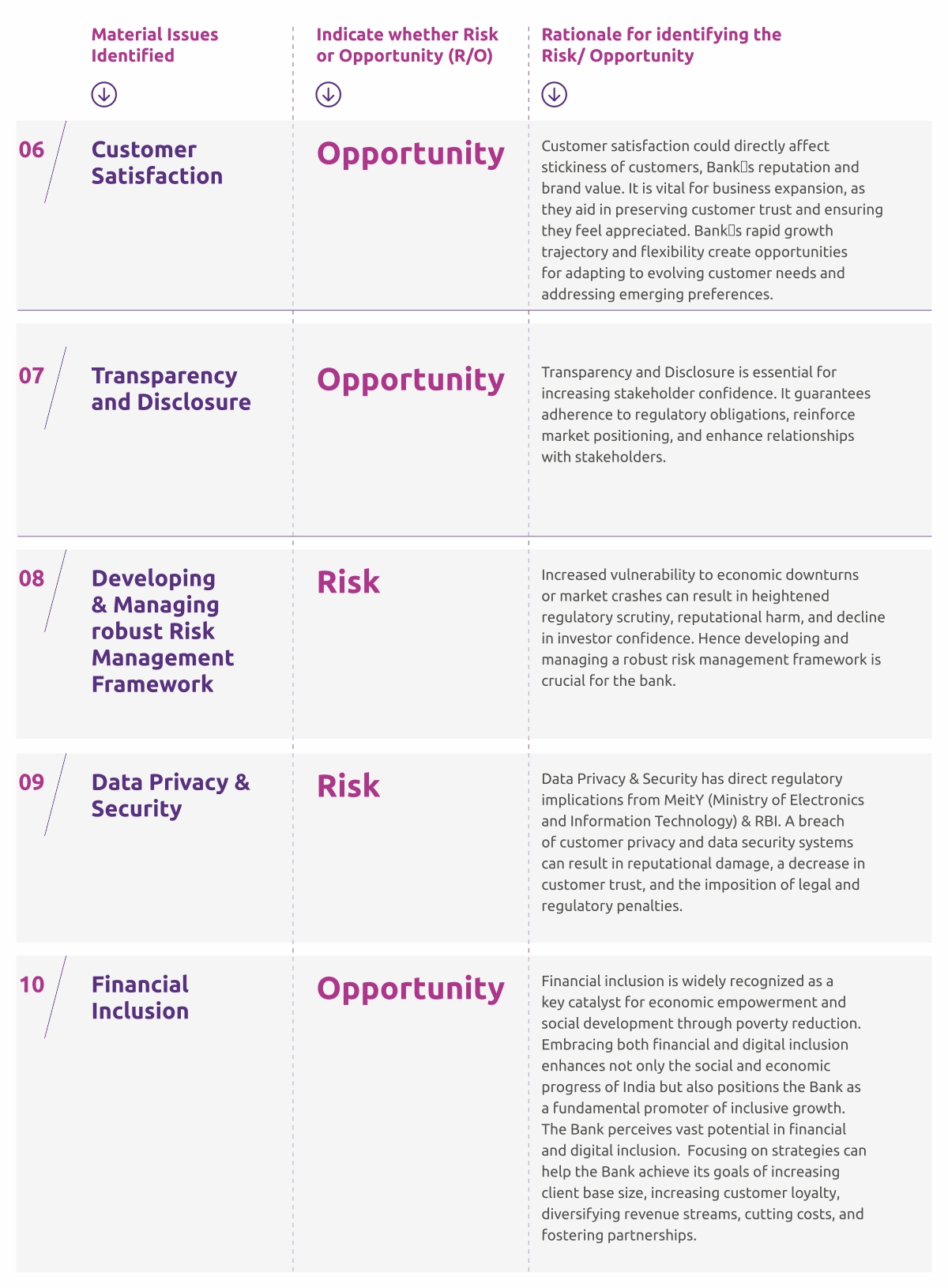
Material Risks & Opportunities affecting Bank’s business strategy in near-and mid-term are as follows:
ESG Strategy
Utkarsh SFB strives to balance financial success with social responsibility and environmental stewardship. Its sustainability strategy outlines a clear roadmap, ensuring that its operations are in step with current ESG trends, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder expectations. By embedding sustainable banking practices, the bank strengthens the adaptability of the financial system, tackles pressing environmental and social issues, and supports the transition to a more sustainable and inclusive economy.
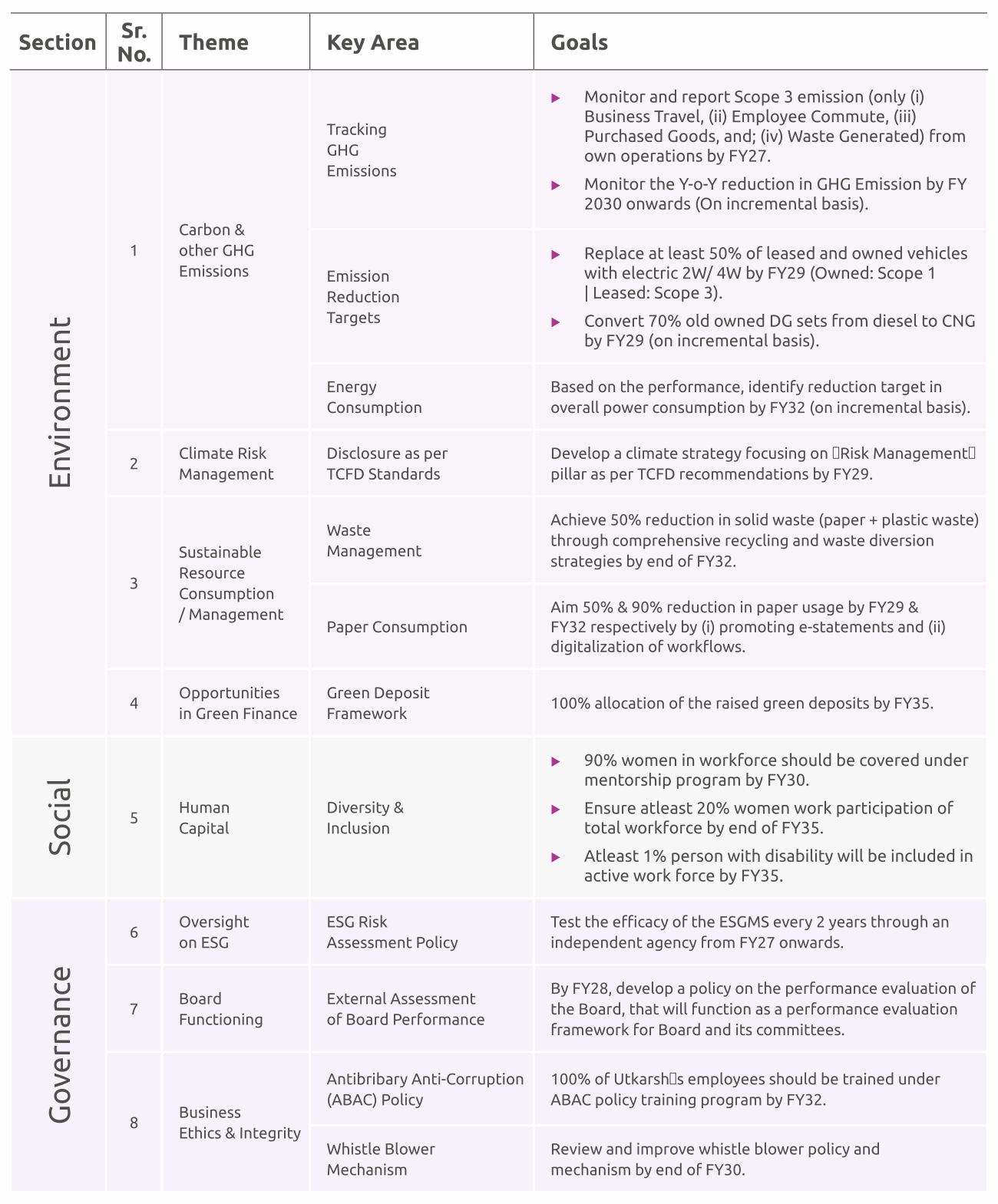
Goals and Targets
Each theme is broken down into key areas aimed at addressing goals and targets as part of the bank’s sustainibility initiatives. The bank has developed a structureed and detailed internal strategy through stakeholder consultation process and is making efforts to achieve its goals accordingly.
- ESG Policy
- Climate Risk
- Sustainable Resource Consumption
- Energy Efficiency
- Digitization / Paperless Initiatives
ESG Policy
An Environmental, Social and Governance\(ESG) Policy
has been developed in alignment with he national E&S regulation, and relevant E&S Good International Industry Practices (GIIP).
The ESG policy also
highlights the applicability of ESG Management System to various financial products.
It guides Relationship and Credit teams to build in caveats to derisk Bank’s loan book from ESG perspective.
The ESG policy includes
ESG Exclusion List
which is based on IFC Exclusion List, a globally accepted best practice.
Bank has a
management level ESG Steering Committee,
which oversees ESG application throughout the Bank.
Bank has also constituted a
dedicated ESG team,
which is mandated to roll out ESG across the Bank in conjunction with Credit, Relationship and Internal Audit teams.
Bank recognises potential adverse environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts arising from financing harmful borrowers’ activities. Bank acknowledges the importance of addressing these risks and impacts systematically.
These adverse impacts, if left unaddressed, could translate to credit risks and/or reputation risks in the long run. Engagements with the borrowers also present opportunities through downside risk management and upside value creation in terms of brand differentiation, portfolio performance, stronger relations, and increased customer stickiness. With this awareness, bank has formulated an ESG Policy demonstrating its commitment to integrating ESG considerations into its business operations.
The ESG policy is given below:
https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/
policy/ESG_Policy_PDF.pdf
The E&S Policy of Bank will be supported by the following operational principles to guide the E&S performance of the bank:

Implementation of ESG Policy
Applicability:The ESG Policies and Principles are formally adopted by Utkarsh Small Finance Bank’s Board of Directors and
is applicable to all loans extended by the Bank from the date of approval.
Communication: The ESG Policies and Principles will be communicated to all employees through suitable training programs and also communicated to other stakeholders, such as investors, borrowers, as relevant. The ESG Policies and Principles may also be disclosed through Utkarsh Small Finance Bank’s website.
Support: The policies are supported by an Environmental, Social & Governance Management System (ESGMS) to achieve the policy objectives. The ESG-MS is formally adopted by the top management and will be implemented in all loan transactions of the bank from the date of approval.
Review & Updates: The ESG Policies and Principles will be reviewed and updated as required, at least once in three years, to ensure its effectiveness, adequacy, and suitability to the changing scenarios of environmental, social and governance.
Audit: The ESG Policies and its requirements will be audited as per the existing Internal Audit processes of Utkarsh Small Finance Bank.
ESG Governance: Details about Steering ESG Committee & Board oversight are given in the Section 8.3 of this report.
Climate Risk
Bank identifies that climate risk as a key risk type, which may affect Bank’s portfolio in medium to long-term. Historically, physical climate risks (viz., floods, draughts or cyclones) have affected Bank’s portfolio performance. Numerous scientific reports suggest that the frequency and intensity of these physical events are likely to rise due to climate change and increased greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Since climate risk is a developing field, the most effective strategies to comprehend the long term financial impact and avoid them, are still being established.
Bank is aware that as a lender to MFI and small MSME category borrowers, its exposure towards physical climate risk may be significantly high.
Hence, transition risk may not be extremely significant at this point.
Reserve Bank of India has come up with a Draft Disclosure framework on Climate-related Financial Risks, 2024 applicable from FY26. This framework
essentially mandates all Indian banks to align themselves with Taskforce for Financial Disclosure (TCFD) guidelines. Bank has set up its governance framework, and is considering to: (i)
integrate climate-related strategy in ESG risk assessment framework and; (ii) develop short, medium and long-term strategy around climate risk etc.
Given that climate risk is expected to affect the exposure book in slow but certain adverse ways; the Bank remains vigilant on how: (a) advance strategy is modified to counter stress on loan book from physical climate risks; (b) how the regulatory disclosure standards come up in Indian context.

Sustainable Resource Consumption
70%
Reduction in water consumption due to Low Flow Fixtures Installation in Utkarsh Tower
Utkarsh Tower is
40%
energy efficient than conventional building.
2,97,35,191
Papers saved in FY24
140 KWP solar PV
offset more than approx.
15%
of annual energy demand.
Bank considers natural resources as an important of business input, and recognizes the global action needed for sustainable consumption. The Bank is committed to continuously improving the resource efficiency of its operational processes. The Bank is committed towards conserving energy by: (i) implementing energy conservation projects, (ii) adopting energy efficient technologies, and (iii) promote usage of renewable energy sources. Energy Performance Index (EPI) for Utkarsh Tower has reduced by 21.35% and Energy Performance Metric (EPM) for branches reduced by 27.74% between FY15 and FY20. Refer to Section 5 for targets related to paper consumption and waste management.
Some of initiatives undertaken at Utkarsh Tower to conserve energy are given below:

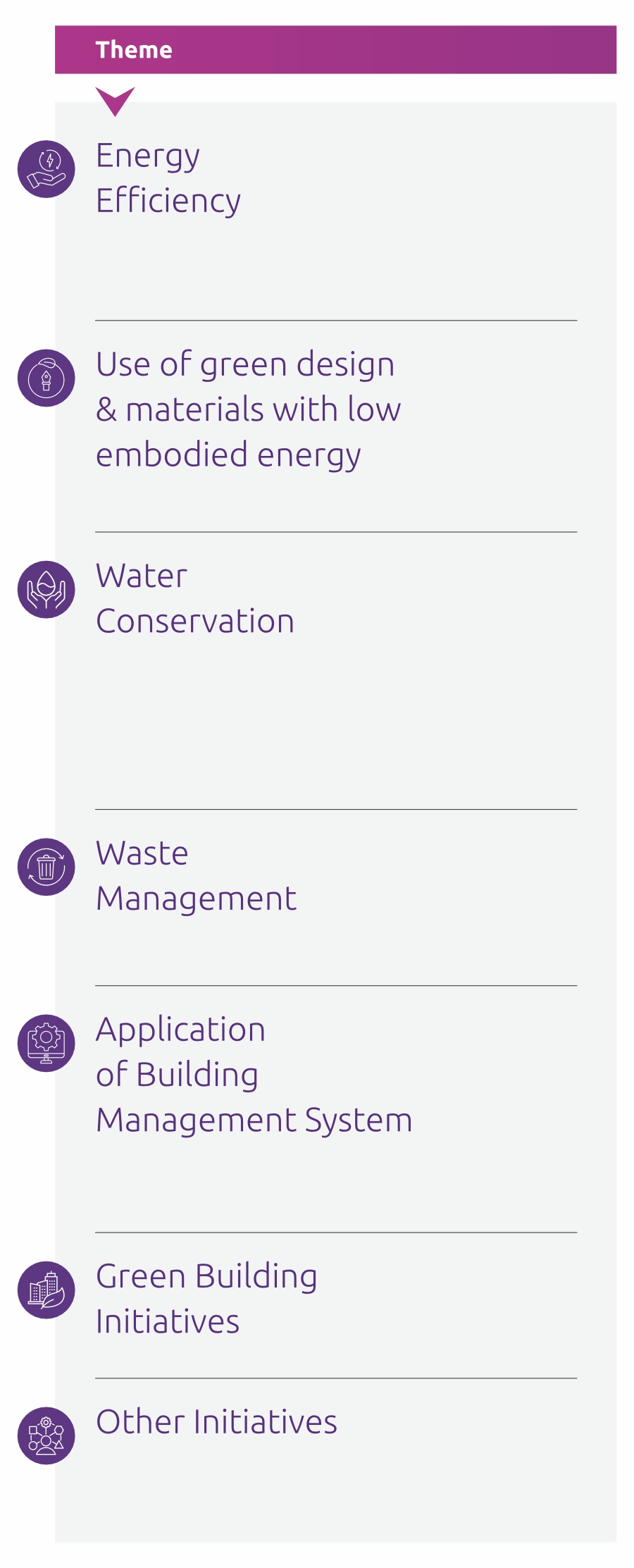

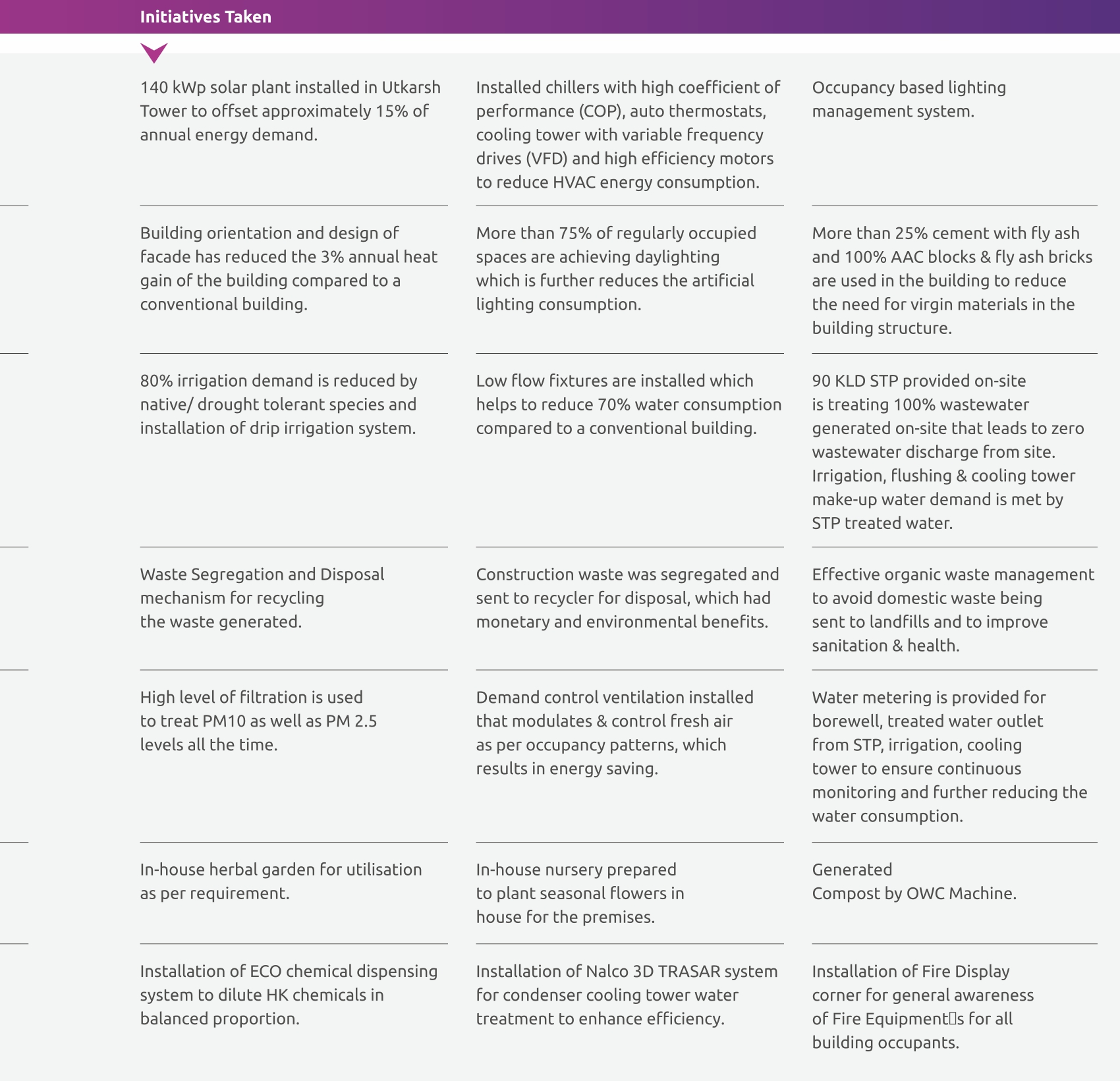
Energy Efficiency
Energy Efficiency initiatives already covered in the section 6.3 of this report. Refer to Section 5 for targets related to energy consumption.
Digitization / Paperless Initiatives
3498
Trees Saved
by saving 2,97,35,191 papers in FY24
21,33,845
Accounts opened till 31st March 2024 through Digi Onboarding
14,135
UPI QR code digital collection for JLG Clients
2.92%
Increase in digital transaction volume on mobile UPI App

UPI App
Bank launched UPI App during FY 2021-22. Utkarsh was among the first SFBs to go live on UPI Lite Application which enables small-ticket transfers of up to Rs.500 far more conveniently. There is a consistent increase in the number of digital transactions on the UPI App.

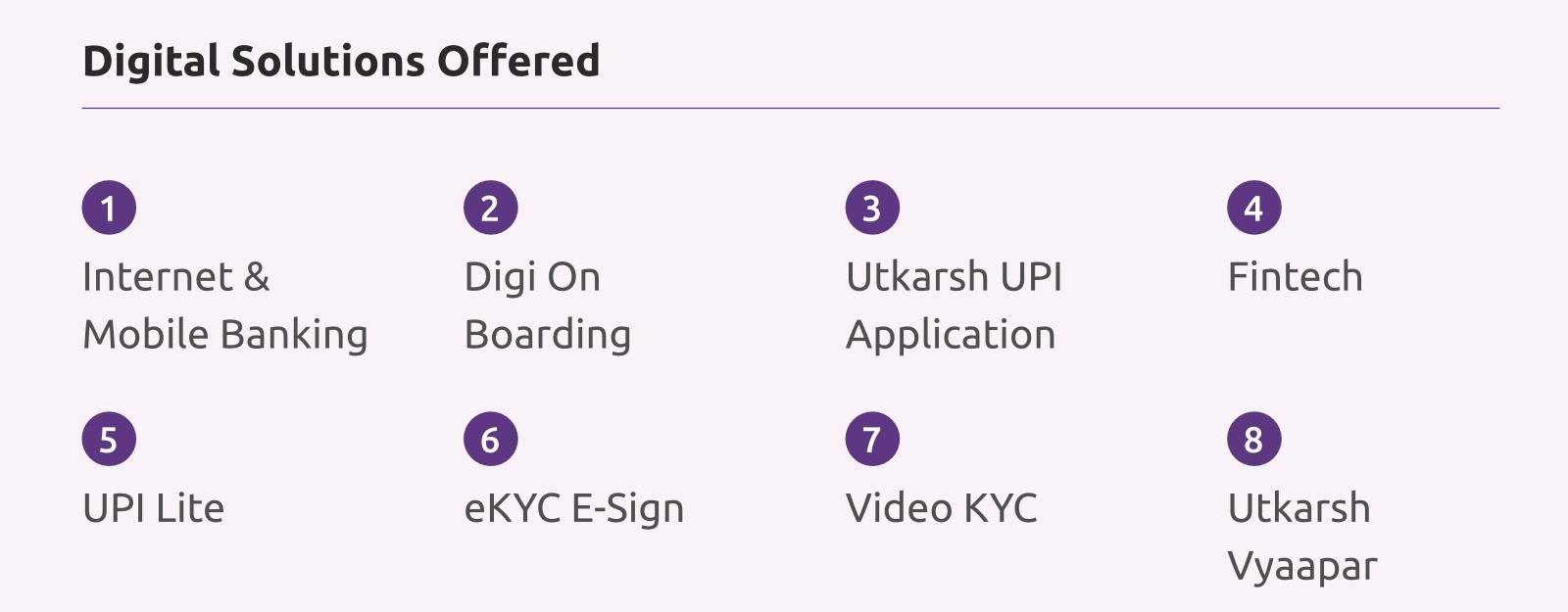
Bank launched digital on-boarding of accounts in the FY 2020-21. Since then bank is continuously taking efforts to on-board customers. While there were challenges in onboarding customers in FY 2022-23, the organization has effectively bounced back and achieved increased engagement with its digital payment services.
Bank has strengthened their data analytics capabilities & digital onboarding process. Strengthening digital offerings with increased investments in technology helped in easy onboarding of customers, reduce operational costs and improve NPAs. The Bank invested in software upgradation in order to stay up to date with advancements in technology.
- Bank’s Human Resource(HR) Strategy & Policies
- Job Creation, Employee Retention & Attrition
- Employee Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI)
- Capacity Development of Employees
- Financial Inclusion
- Bank’s CSR Strategy & Policy/Community Engagement
- Impact of CSR Projects
- Customer Satisfaction & Grievance Handling
- Customer Centricity & Product Innovation
Bank’s Human Resource(HR) Strategy & Policies
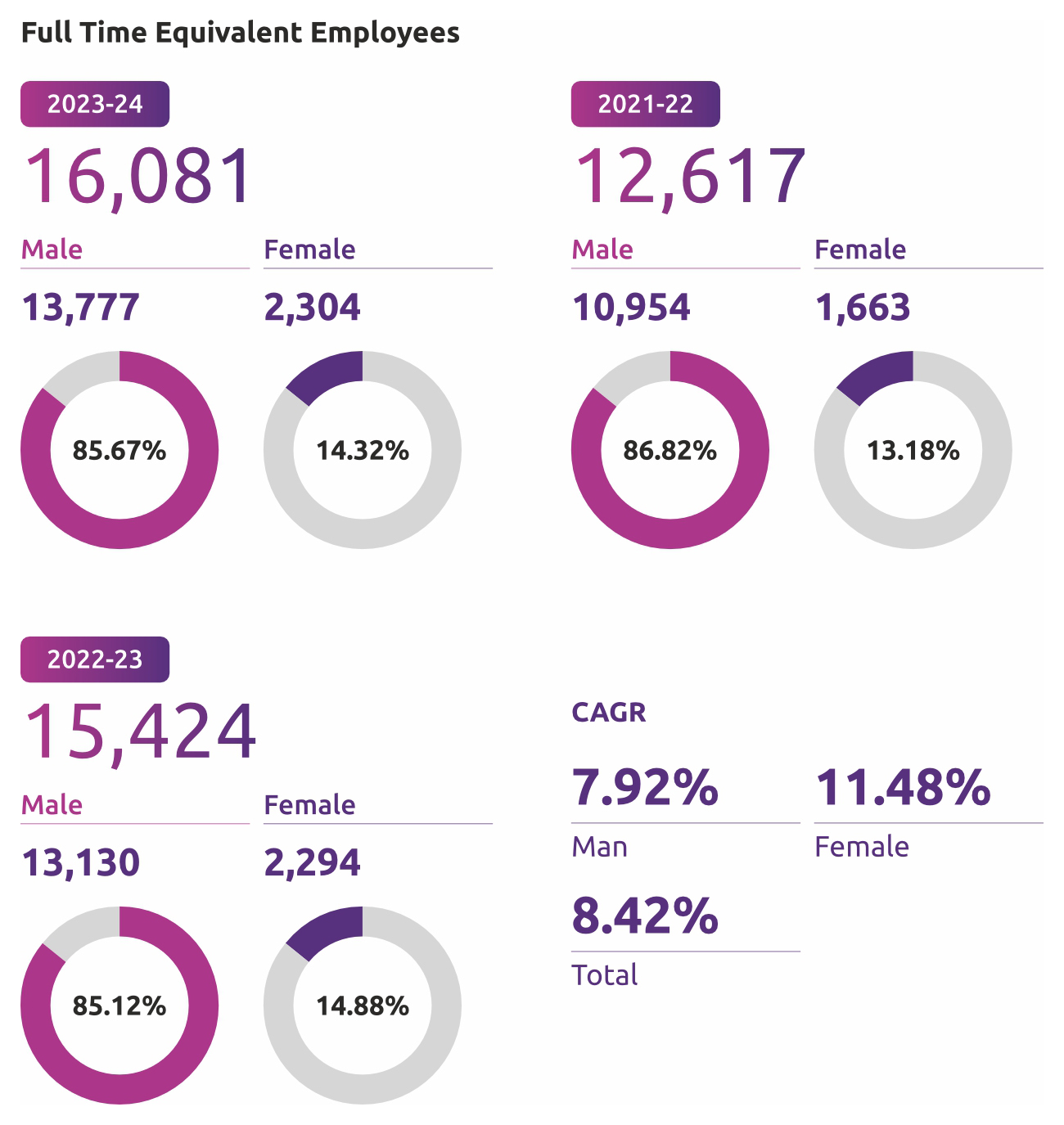
Employee Base
Employee count has grown to
16,081
full-time equivalent(FTE) employees,
comprising people from diverse backgrounds and experiences.
Organisational Citizenship
Bank awarded
562
employees
in FY 23-24 for completing 5 years with the organisation through the Long Service Award.
Human Resources Policy of the Bank was approved by the Board of the bank on 09 January 2017 and the same has been reviewed by the Board of Directors in its meeting in 22 March 2022 pursuant to the guidelines issued by RBI, to cover all employees of the Bank.
HR is integral to realizing the bank’s goals, from recruitment to talent retention and engagement. Bank’s HR Policy aligns with its vision and mission, fostering employee motivation and work-life balance. Risk mitigation measures are in place for employee conduct. Bank prioritizes learning, skill development, and teamwork, facilitated by technology-driven HR services. A collaborative and peopleoriented culture promotes diversity and sustainable growth.
Since 2022, Bank has adopted a digital platform for employee lifecycle management called Digidesk. Bank’s performance management system is fully automated, handling goal setting and appraisals. Digidesk streamlines onboarding with digital ID issuance, electronic signatures and easy access to forms, eliminating paper documentation.
Employee Engagement
Bank is aware of the instrumental role played by employee engagement in creating a culture of excellence in the organisation. Bank has robust engagement channels that allows their employees to share their feedback and suggestions. Bank has implemented an online grievance redressal platform to address grievances of employees in a transparent and time-bound manner. Bank has a seamless online HR query helpdesk to answer the queries of all employees. Bank also has Employee Grievance Redressal Policy which highlights formal process for registering employee grievance.
Bank believes in recognising the efforts of their employees fairly by adequately compensating them based on their performance, both short and long term. Employee benefits like interest-free advance against salary, housing loan, bike loan, mobile loan, personal loan and adequate insurance cover enables employees to focus on work without having to worry about any hassles. Bank also recognises best performers and elebrate organisation citizenship behaviour through various awards for innovation, risk mitigation, vigilance and customer service, among others.
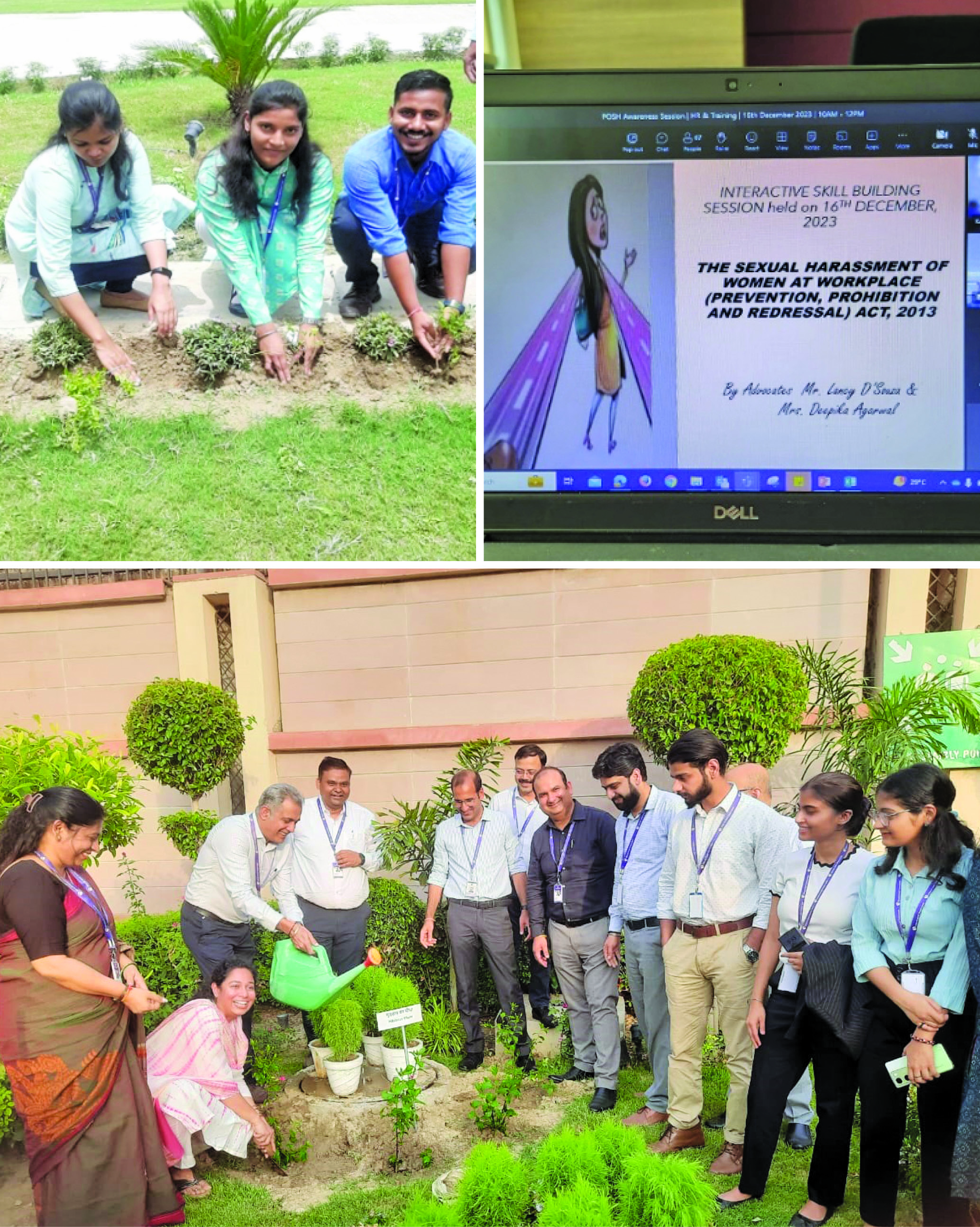



as necessary and formulation of policy thereon. It also undertakes a process of due diligence to determine the suitability of any person for appointment /continuing to hold appointment as a Director on Board, based upon qualification, expertise, track record, integrity other ‘fit and proper’ criteria, positive attributes and independence (if applicable) and formulate the criteria relating thereto.
Renumeration
Nomination & Remuneration Committee & Board looks after process for determining remuneration. The remuneration of employees in control functions such as Risk and Compliance depends solely on their individual and overall functional performance and is not linked to any business outcomes. The same is also reflected in their KRA’s. Based on the performance review at an organisational / Functional / Individual level, the bank decided on percentage of salary increments to be given at various levels of performance of each individual employee.
Bank also has in place a Policy on Risk Alignment of Compensation applicable for MD & CEO and Risk and Compliance staff.
Governance of HR Issues
Nomination and Remuneration Committee reviews the code of conduct and human resources strategy, policy and performance appraisal process within the bank, as well as any fundamental changes in organisation structure. The NRC Committee details can be viewed at: https://www.utkarsh.bank/about-us#pills-committees-of-bank-tab
Nominating & Selecting the Highest Governance Body:
Nomination and Remuneration Committee (NRC), as the principal governance authority, proposes the appointment of bank directors to the Board, pending approval from the Board itself. For director selection process, NRC review the structure, size, composition, diversity of Board and make necessary recommendations to Board with regard to any changes
Based on the performance review at an organisational / Functional / Individual level, the bank decides on percentage of salary increments to be given at various levels of performance of each individual employee. The ratio of the remuneration of each Director to the median remuneration of the employees of the bank for the FY24 can be accessed in the annual report
Non-Executive Compensation Policy is publicly available on website at:
https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/pdf/our-policy/template_ten/Non_Executive_
Compensation_Policy.pdf
Job Creation, Employee Retention & Attrition
8.42%
Three-Year Employee Growth CAGR
11.48%
Three-Year Female Employee Growth CAGR
Empowering Fresh Talents
Bank conducts weekly hiring of freshers from tier-2, tier-3 cities, and villages, enrolling them in a comprehensive 15-day training program. This program equips them with banking knowledge and employability skills, leading to their employment at the bank. The bank has also recently tied up with a leading university and launched the ‘Probationary Officers Program’ for graduates with an objective of grooming young talent and make them job-ready and subsequently absorb them in the bank across different roles. The bank takes pride in the fact, that it has nurtured and will continue to nurture thousands of aspiring youngsters and grow them into future bankers.
Employee Recruitment
The growth of FTEs across last three FYs is shown below. It can be observed Y-o-Y total FTE number has grown at a CAGR of 8.42%, while the number of female FTEs during the same tenure has grown by 11.48% CAGR.

Employee Turnover Rate
It can be observed from the table below that the employee turnover rate in last three FYs has grown by a CAGR of 7.7%. To compensate this Bank has stepped up its recruitment process

Employee Retention
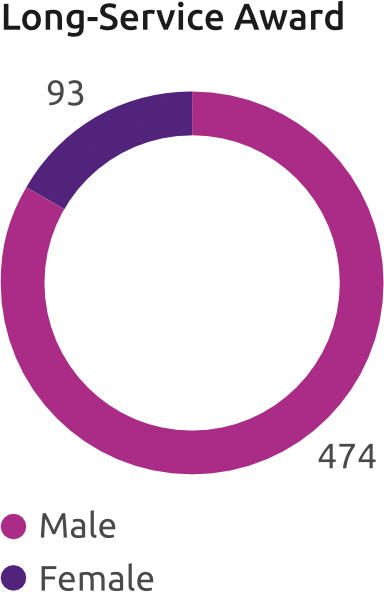
Bank awards its employees every year for completing 5 years with the organisation through the Long Service Award. In FY24, Bank awarded 562 employees with Long-Service award. The number of employees completing five years is given below:

Parental Leave
In FY24, 474 female employees underwent maternity benefit whereas 93 male employees undertook paternal benefits. Out of this, 97% of employees have returned back to the organisation

Employee Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI)
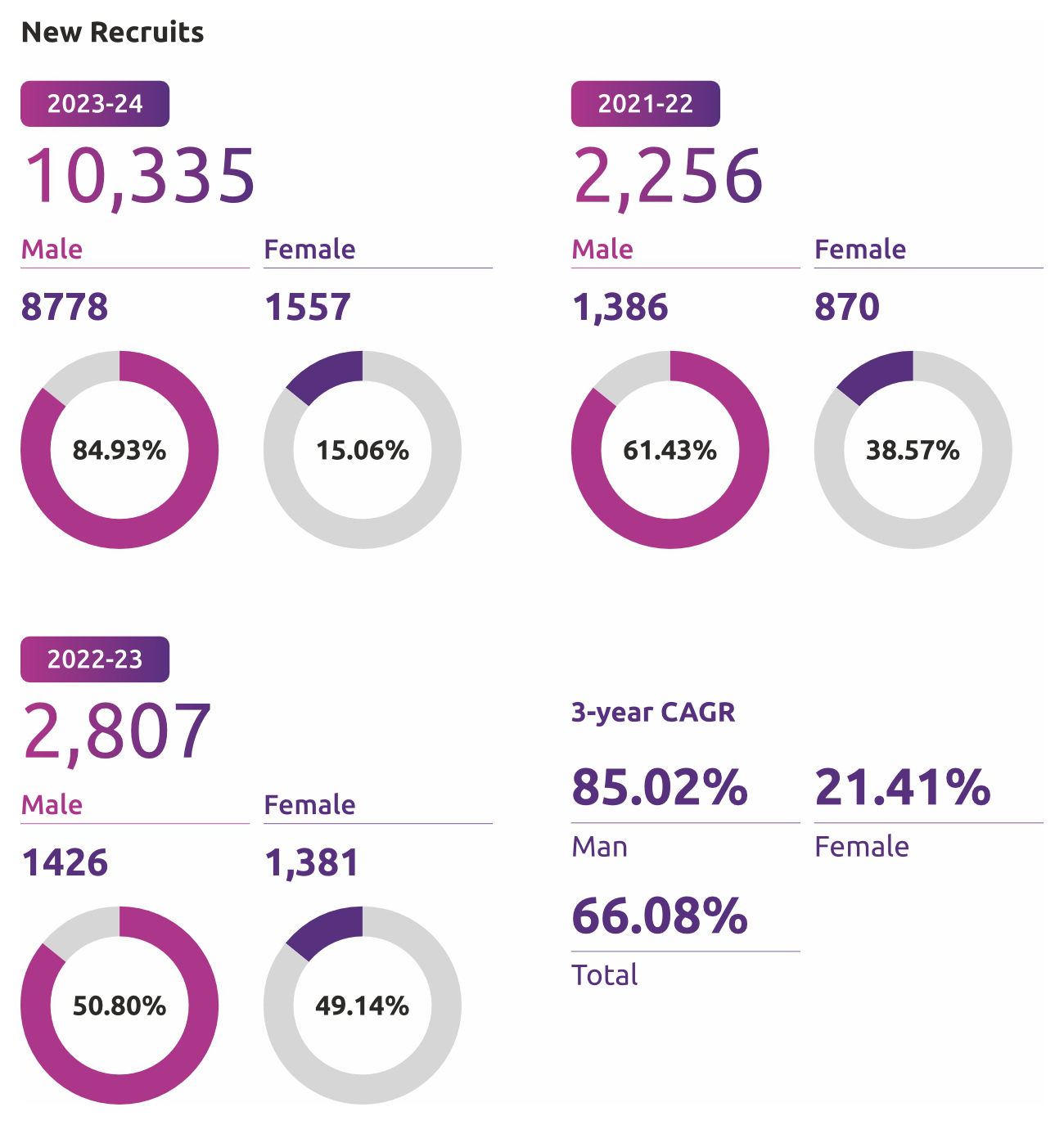
10,335
New Recruits in FY24
21.41%
CAGR of Female New-recruits over the three-year period
38.67%
Growth in movement of females from lower to middle level management in last three FYs
Bank believes that a diverse and inclusive approach is essential for a sustainable growth. It fosters a culture of diversity, equity, and inclusion, recognizing that a workforce with varied backgrounds and perspectives leads to better decision-making and ultimately, better outcomes for the customers.
Bank’s commitment to human capital is unwavering, and it will continue to prioritize it as they grow and evolve further as a bank. During FY 2023-24, Bank added 10,335 employees, of which, 1,557 were female employees. Refer to Section 5 for targets related to diversity and inclusion.
All employees of the bank hold Indian nationality
Zero cases of incidents on discrimination and incidents of violations involving rights of indigenous peoples were reported in FY 2023-24.
Gender Disaggregated Recruitment data
In last three years, total number of new recruits grew significantly at a CAGR of 66.08%. The female recruits increased at CAGR of 21.41%, whereas male recruits grew at a rate of 85.02%


Age-Wise Diversity
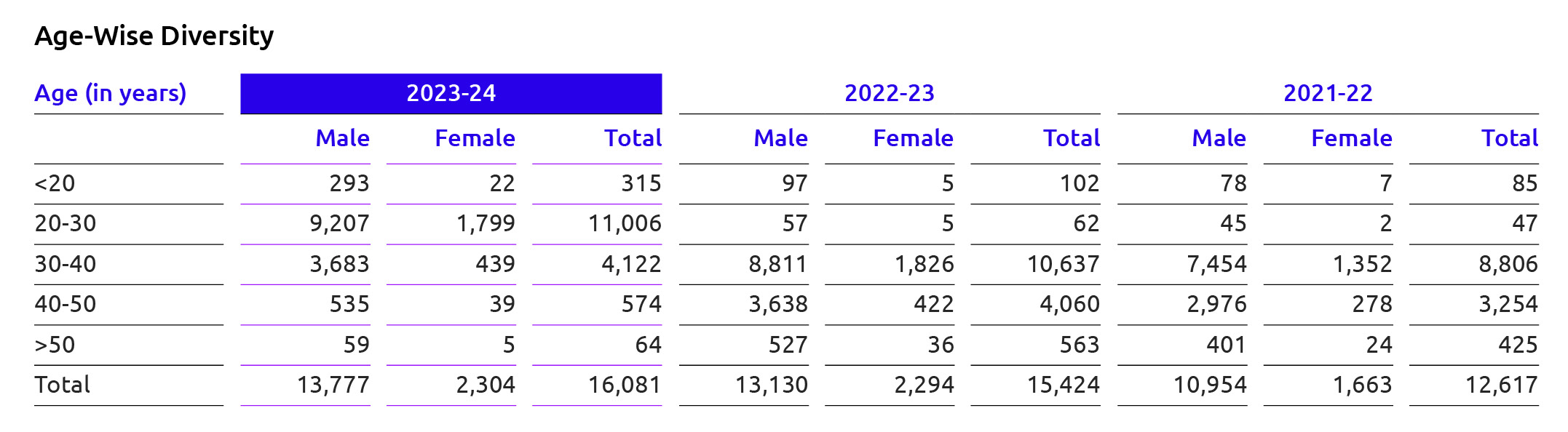
The number of male and female employees in 20 age group increased notably, indicating a positive trend in early career hiring and gender diversity efforts. There’s a significant increase in both male and female representation in the 20-30 age group, reflecting Bank’s robust recruitment drive and gender-inclusive hiring practices for young professionals.
Bank has taken efforts towards gender diversity across different age groups, with variations in workforce composition influenced by factors such as recruitment strategies, career progression, and retention initiatives. There is a significant increase in young employees (especially in the 20-30 age group), indicating a strong
recruitment drive targeting younger talent. However, there’s a notable decline in the 30-40, 40-50, and >50 age groups, which may indicate challenges in retention or a shift in workforce demographics.

Management-Level-Wise Gender Diversity
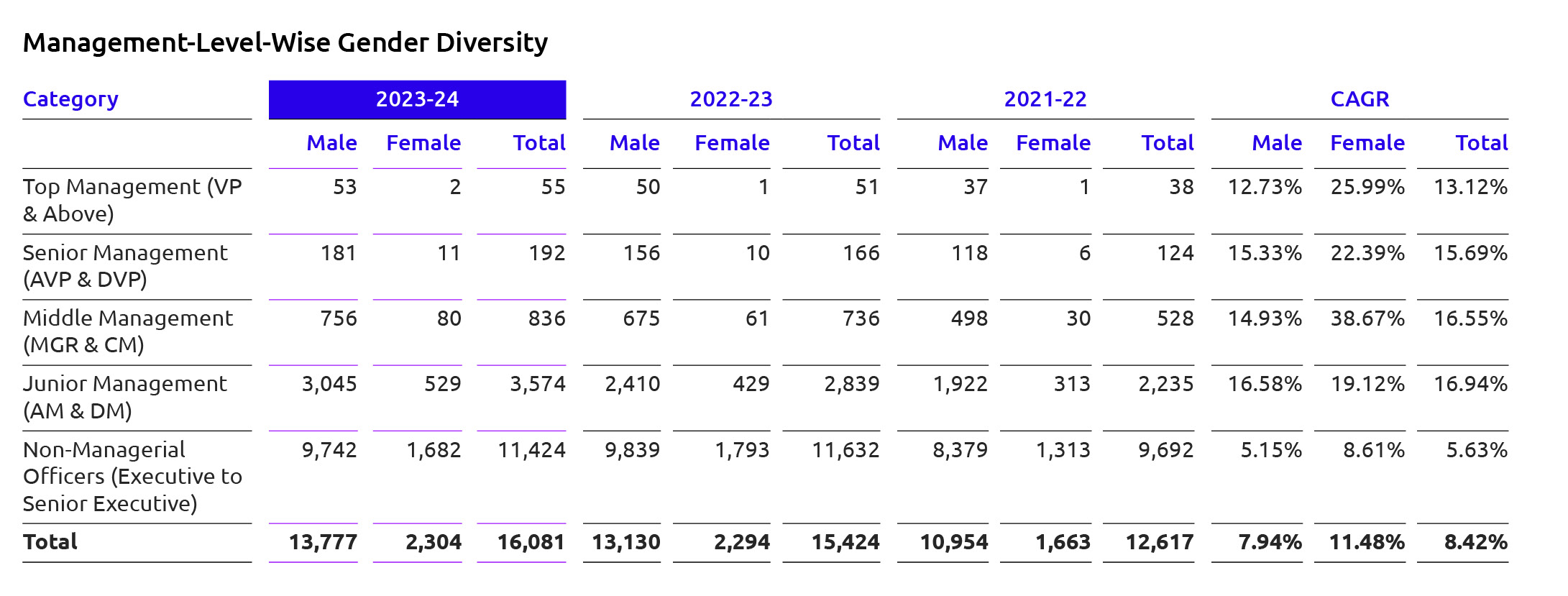
There is positive trend towards gender diversity and inclusion across all management levels, with increasing representation of females over the years. However, there is still room for improvement, particularly in achieving more balanced gender ratios, especially at higher management tiers. At Junior
Management level, both male and female representation has increased, with CAGRs of 16.58% for males and 19.12% for females. A notable increase in female representation at middle management level can be seen with CAGR at 38.67%.
All the senior management level employees are hired from local community based on their skills and expertise.
Bank implements inclusive hiring practices from the initial stages of recruitment, avoiding discrimination based on attributes unrelated to job requirements, such as physical challenges, age, gender, religion, marital status, or any other irrelevant features.
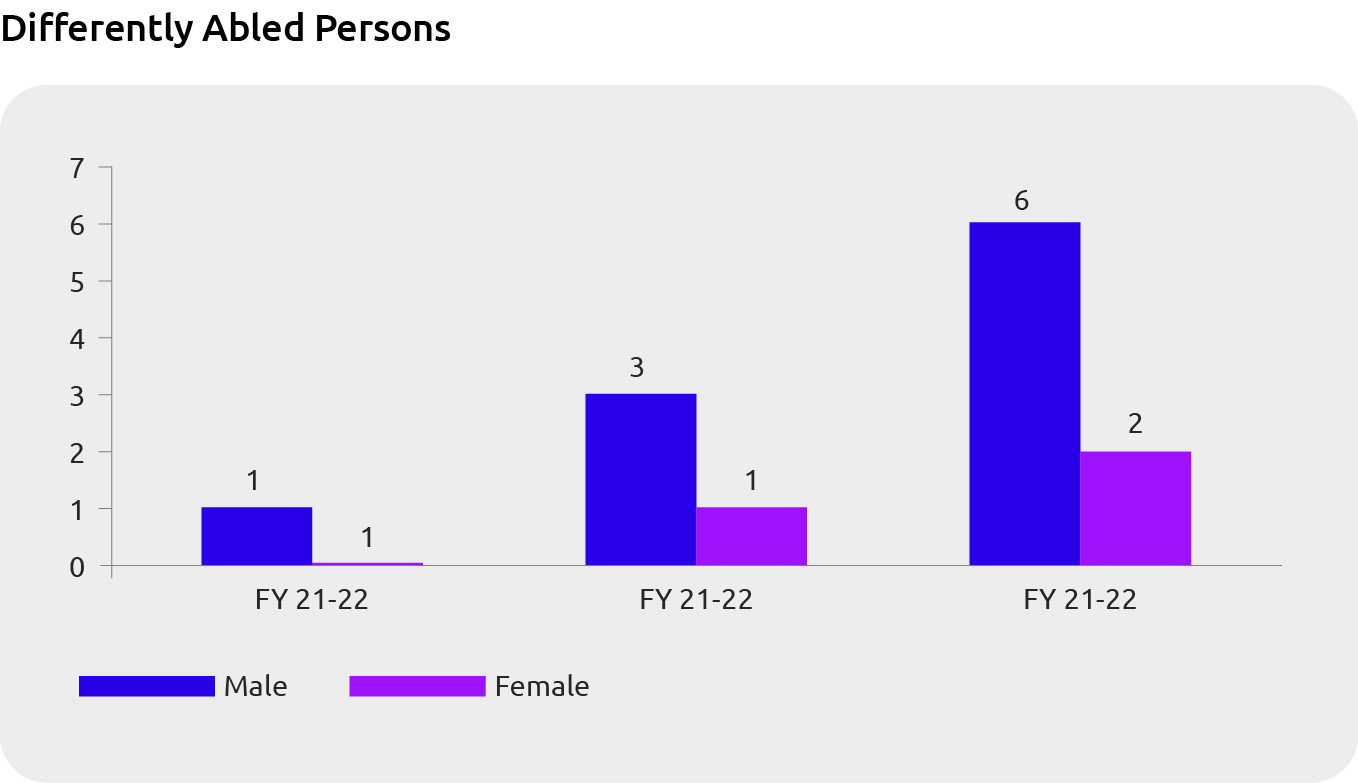
In FY24, the bank employed 8 individuals with disabilities, doubling the count from FY23, and ensured a safe and inclusive work environment where all employees can develop and thrive.

Capacity Development of Employees
29.2 hours
Average Training Hours per Full-time equivalent Employees in FY24
CEO & CXO Mentoring Club
In FY 2022-23, Bank initiated mentoring club for senior management wherein selected employees are groomed by engaging them in various meaningful projects
In FY 2023-24,
4
Employees were selected for CEO Mentoring Club.
5 Directors
Trained on Programs on governance and assurance, Enhancing Board Focus on Enterprise Risk Management, Familiarization Program for Independent Directors.
As part of the talent management initiative, bank organised for the senior management team.
a vision execution workshop,
and identified a list of competencies based on which a
‘360-degree feedback’
was conducted
for the senior management team.
972 Employees
Trained on ESG Policy & Guidelines, Ethical conduct, Disciplinary Procedures, Employee Benefits.

Bank’s strength lies in the key competencies of its employees. With shifting customer preferences, technological advancements, and banking techniques, the organization needs to keep employees’ competencies and skillset up-to-date. Utkarsh takes consideration in providing the necessary on-the-job trainings to all employees on a regular basis, enhancing their skillset and enabling their professional growth.


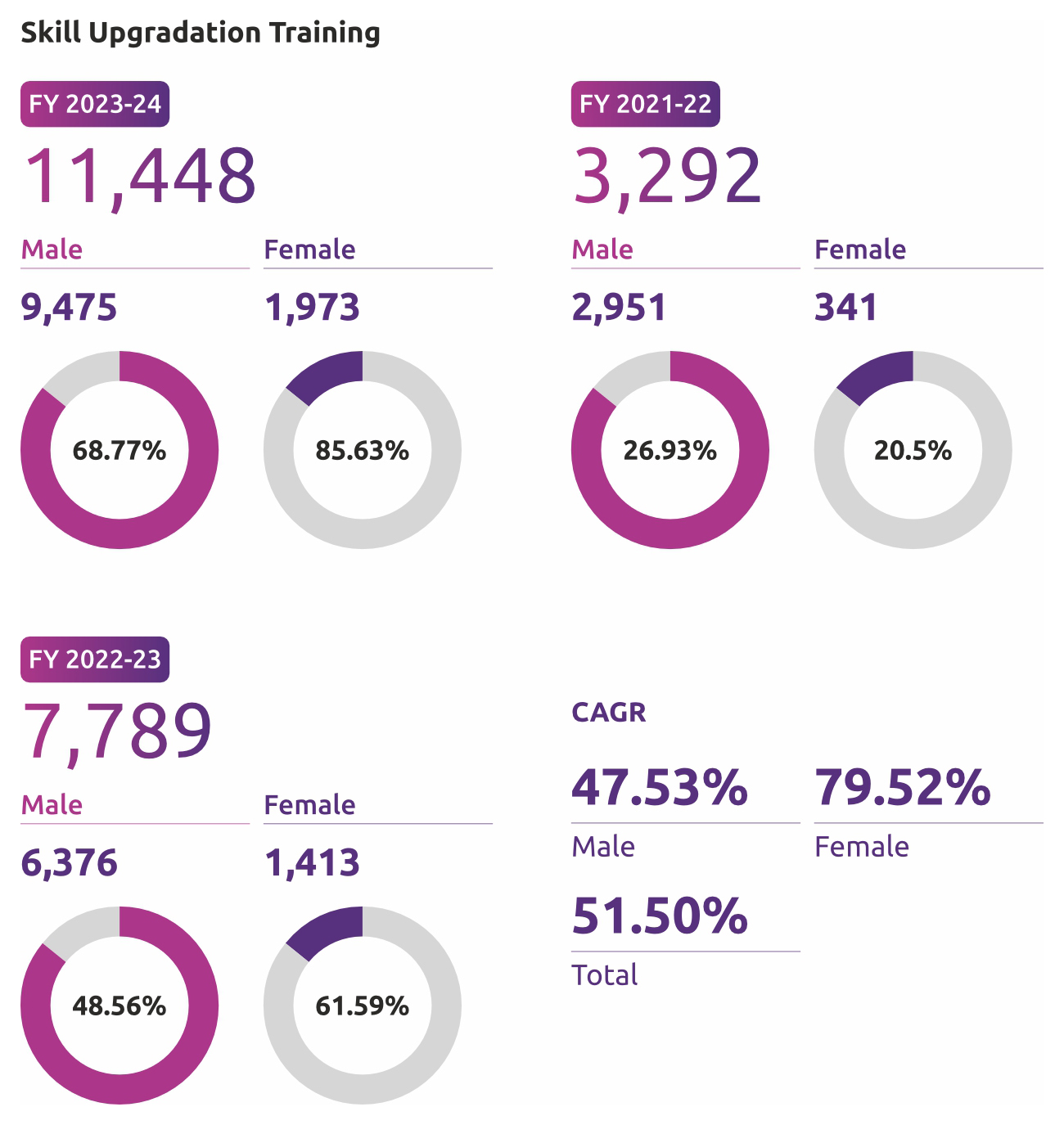
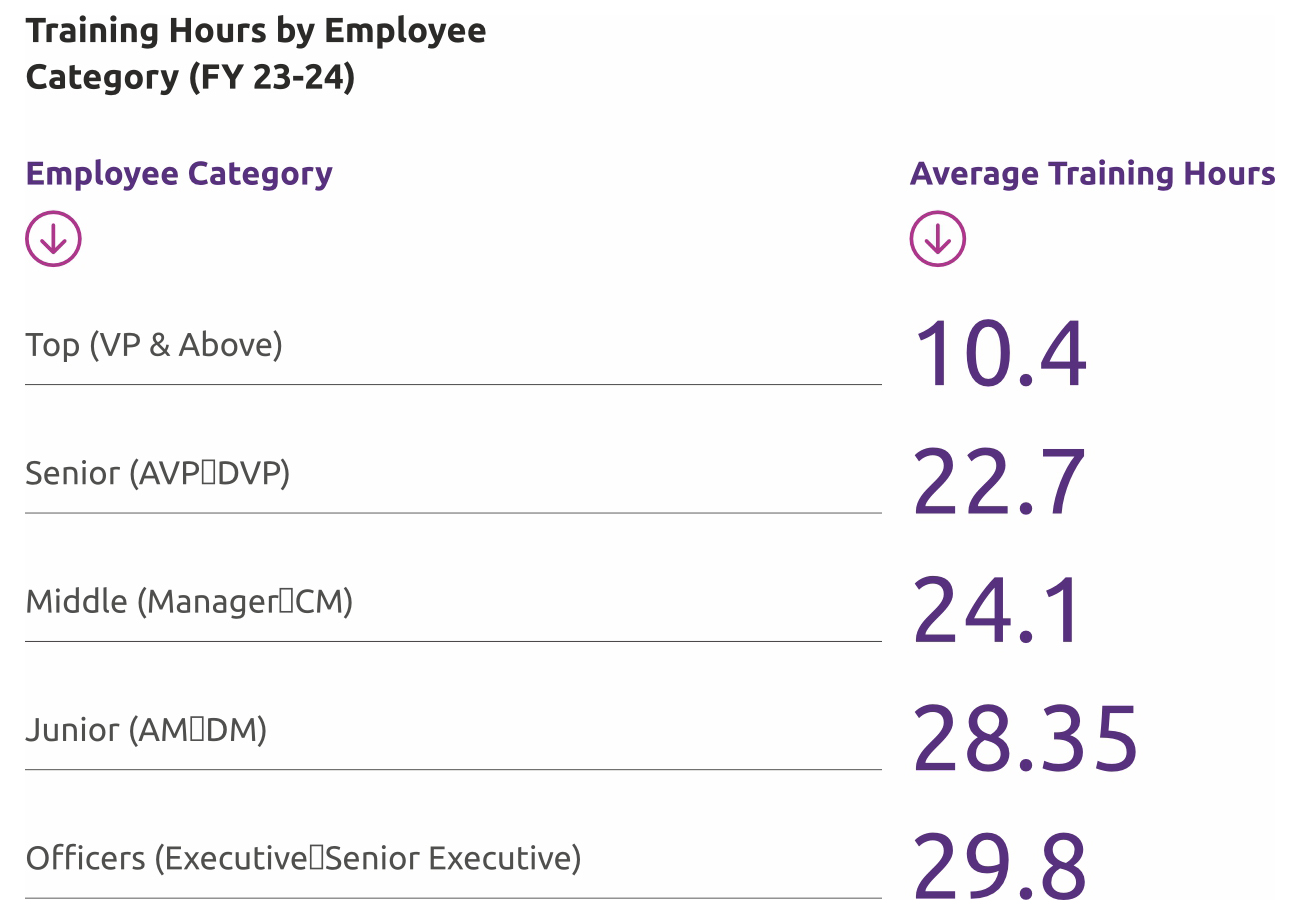
Bank prioritizes skill training for its employees, achieving a 51.50% CAGR in employee upskilling over the past three years. During this period, female employees experienced a 79.52% CAGR in upskilling, while male employees had a 47.53% CAGR. Skill enhancement remains a focal point, with 16,081 employees participating in diverse training programs, averaging 29.2 hours of learning per employee. A total of 71.18% of employees were covered under various skill upgradation programs in FY24.

Average Number of Training Hours
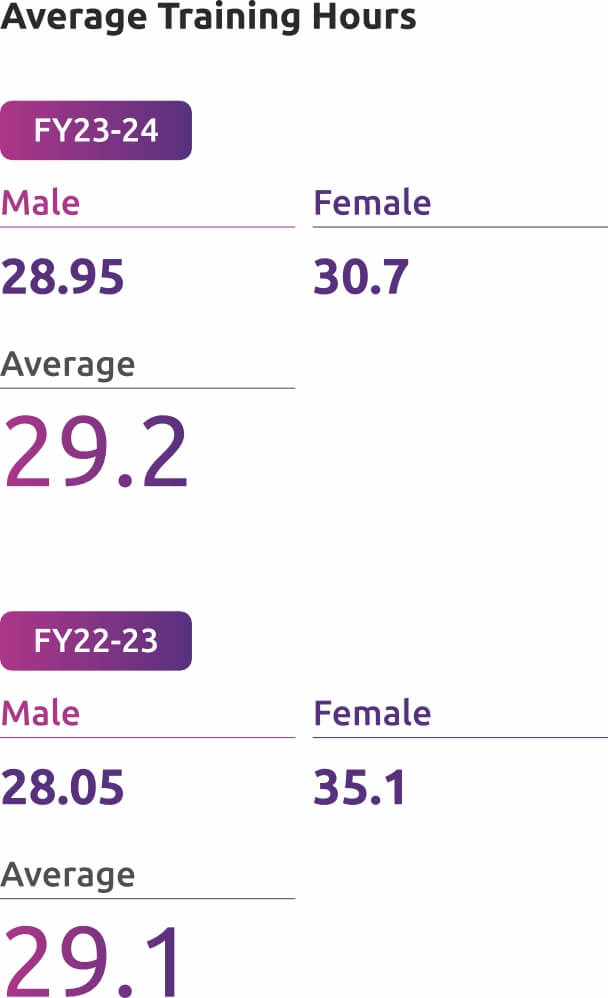
972 Employees were trained on ESG Policy & Guidelines, Ethical conduct, Disciplinary Procedures, Employee Benefits etc.
In FY 23-24, the average training hours varied by employee category is given below:

Financial Inclusion
62%
Micro-Banking Loans
30+ Lakh
Micro-Finance Borrowers as on 31st March, 2024
86%
Micro-Banking Branches
Bank transitioned from a NBFC-MFI into a Small Finance Bank and commenced SFB operations from January 23, 2017. Bank aims to promote financial inclusion and provide access to banking services to underprivileged, underserved and unbanked sections of the society such as women entrepreneurs, low-medium-income households, micro and small enterprises, and affordable housing.
MFI Lending
Growth of MFI borrowers over last three FYs:

CAGR
9.01%
Out of Bank’s 888 total banking outlets, 612 are micro-banking During FY24, Bank opened 58 branches, out of which 33 were MB branches. Micro-Banking loans have increased at 18% CAGR over last four years (FY20-FY24). 62% of the loan book consist micro-banking loans. 86% Micro-banking branches are in rural & semi-urban areas. Micro-banking branches are spread across 13 states and further. In addition, the Bank is expanding its presence to other states / geographies.
Micro-banking portfolio crossed
₹ 11,000 Crore
mark
Bank’s MFI customer base is growing at a CAGR of 9.01% in last three FYs. This consistent growth indicates a rising trend in the utilization of microfinance services, potentially driven by increasing financial inclusion efforts of the bank and the need for accessible credit among underserved populations. The steady expansion of MFI lending underscores bank’s crucial role in addressing the financial needs of marginalized communities and fostering economic empowerment at the grassroots level.

Leading States in JLG Portfolio
There is robust growth of JLG portfolios in these states, reflecting the effectiveness and popularity of lending mechanisms in fostering financial inclusion and empowerment at the grassroots level. Despite being fourth among the top five states, Jharkhand demonstrates the highest
growth rate, with a remarkable CAGR of 19.90% over three-year period. Bihar leads with the highest number of active loan clients across all three fiscal years, showing consistent growth with a CAGR of 8.44%.
Keeping in view the objective of the Bank to serve the underserved and unserved, Bank has adequate presence in the less financial penetrated areas of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand etc. These geographies offer the potential for growth for microfinance business and financial inclusion related opportunities.

Average Ticket Size of Gross Loan Portfolio
There is significant growth across various loan product segments, with particularly noteworthy expansions in MB loans. With a substantial increase from 0.3 lakhs in 2022 to 0.4 lakhs in 2024, the average ticket size for MB loans exhibited robust growth at a CAGR of 10.06% over the three-year time period.
Priority Sector Lending (PSL) Norms
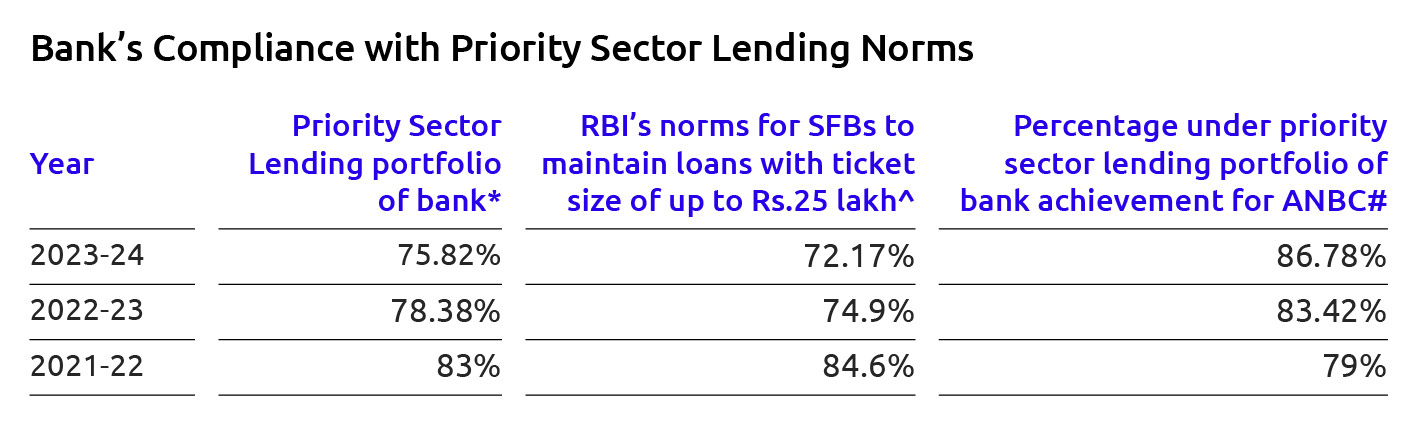
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated a higher priority sector lending requirement for SFBs at 75% vs. 40% for universal banks. Owing to the Bank’s legacy of serving under-banked population of the country and promote financial inclusion, Bank meets PSL requirements set up by RBI, comfortably while monetizing surplus PSL portfolio through sale of Priority Sector Lending Certificate (PSLCs) or sale of surplus PSL portfolio through IBPC (Inter Banked Participation Certificates) / portfolio sell-down. As of 31 March 2024, around 86% of the Bank’s loan portfolio qualified for priority sector lending (PSL norms).
SFBs are required to achieve a PSL portfolio at 75% of the previous year’s ANBC (Adjusted Net Bank Credit). On overall basis, after netting of PSLC sale / IBPC, the Bank’s PSL achievement stood at 86.78% during FY 2023-24, against the regulatory minimum requirement of 75%.
Furthermore, Bank is comfortably placed on RBI’s norms for SFBs to maintain loans with ticket size of up to RS.25 lakh at least 50% of the Bank’s total loan portfolio. The Bank’s lending to the ticket size of less than Rs.25 lakh was at 72.17% of the loan portfolio as on March 31, 2024

Bank’s CSR Strategy & Policy/Community Engagement



Bank’s CSR philosophy is based on cardinal principle to make a meaningful and measurable impact in the lives of economically, physically and socially marginalized communities of the country. The Bank’s strategy is to integrate its activities in community development, social responsibility and environmental responsibility and encourage each business unit or function to include these considerations into its operations.
Bank recognizes the importance of good corporate governance and corporate social responsibility in promoting and strengthening the trust of its shareholders and other stakeholders. Bank undertakes continuous efforts to positively impact the society particularly the underserved and the underprivileged communities in the area of its operations. In accordance with Section 135 of the Act, the Board of Directors on the recommendation of CSR Committee had approved the CSR
Policy which provided for the activities to be carried out.
The CSR Policy is available on the Company’s website: https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/pdf/disclosures/template_eleven/CORPORATE_SOCIAL_RESPONSIBILITY_POLICY.pdf
CSR Policy covers the entire process by which an organization approaches, defines and develops its relationships with stakeholders for the common good, and demonstrates its commitment in this regard by adopting appropriate strategies and projects. Thus, CSR is not charity or mere donations but a way of giving back to society by going beyond business as usual, creating shared value and contributing to social and environmental good.
Bank’s CSR activities will be driven by a dedicated CSR team under the guidance and support of senior functionaries, in particular, the MD & CEO. The CSR Committee would play a significant role in ensuring that the CSR Policy is embedded across the bank’s operations and the CSR initiatives are in line with this Policy. CSR Committee details can be viewed at: https://www.utkarsh.bank/about-us#pills-committees-of-bank-tab

CSR Footprints
Bank expends the CSR funds on certain prescribed activities through Utkarsh Welfare Foundation (“UWF”), a company registered under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 and eligible to undertake CSR activities.
The Bank’s CSR activities shall be on thematic areas of CSR intervention as per Annexure-1, mentioned in the policy document. During the year under review, the Company spent /contributed ₹ 3.40 Crore towards aforesaid CSR projects. Bank undertook the following activities as a part of its CSR initiatives for the FY 2023-2024 as approved by the Board of Directors of the Bank:
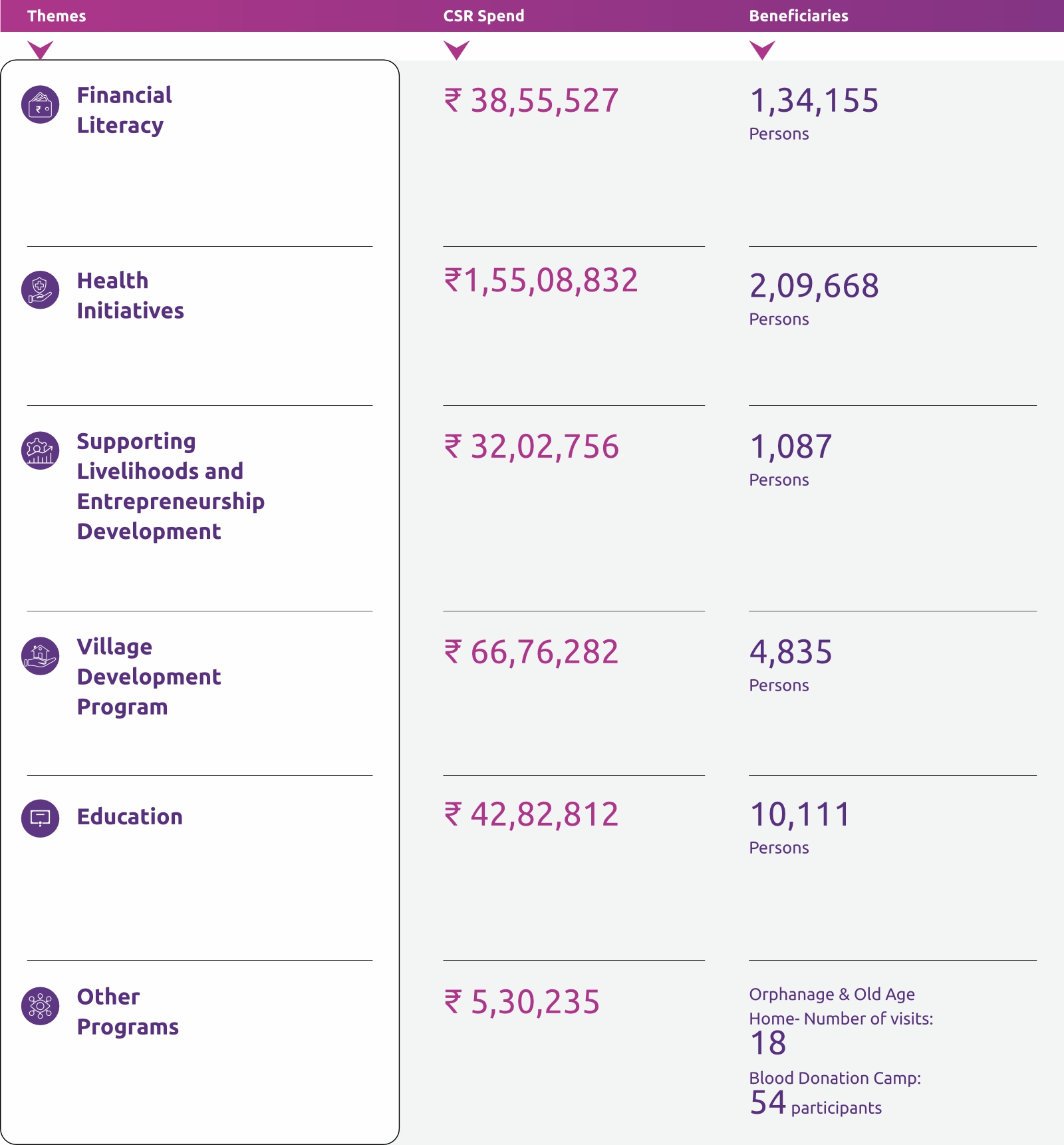

Impact of CSR Projects


Entrepreneurship Development
Provided handholding support to 412 women by providing specialized training through ICAR and establishing their livelihood. The rural women have been able to increase their income by 274.2%

Customer Satisfaction & Grievance Handling
Customer Satisfaction Survey
Bank periodically conducts formal and informal customer satisfaction survey. Recently, Customer Satisfaction Survey as conducted in FY23. The NPS of 21 considered as “Good” from a range of (-100 to 100), derived from a significant sample size of 6,196 respondents, indicates a positive customer perception and satisfaction. This score, validated by the large number of participants, shows more promoters (2231) than detractors (929), reflecting a strong base of satisfied and loyal customers. /p>
Grievance Handling
Grievance Redressal Policy aims to provide a structured mechanism for receipt/resolution of customer complaints and an efficient review mechanism to improve product/service delivery based
on review/analysis of complaints. The policy is a guidance document for timeframe for compliant resolution. Such timeframe is provided separately as well on:
https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/pdf/
comprehensive/Timeframe_for_Complaint_Resolution.pdf
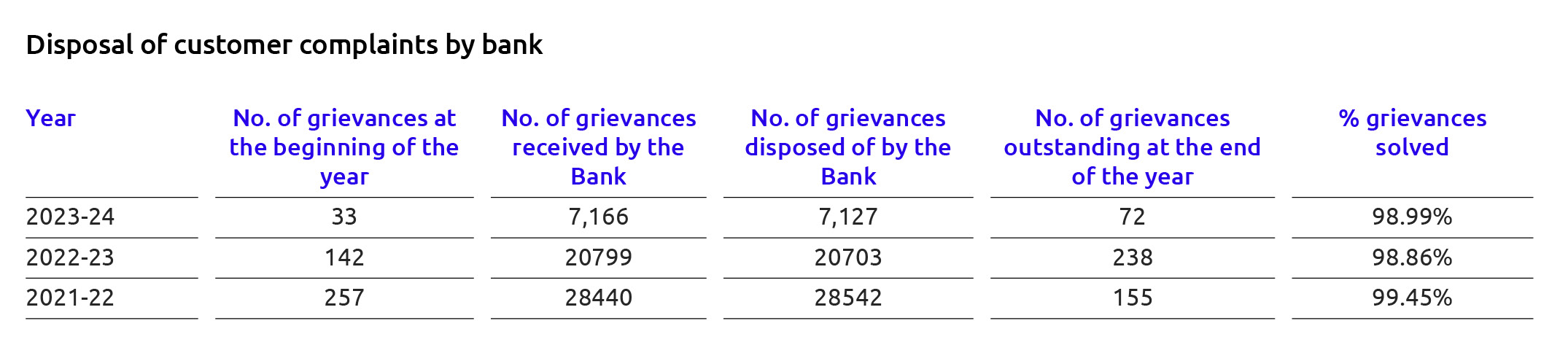
The Grievance Redressal Policy is available on bank’s website: https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/policy/Grievance_ Redressal_Policy.pdf
For monitoring and reviewing customer service delivery & grievance redressal mechanism, bank has internal review mechanism consisting of following committees:

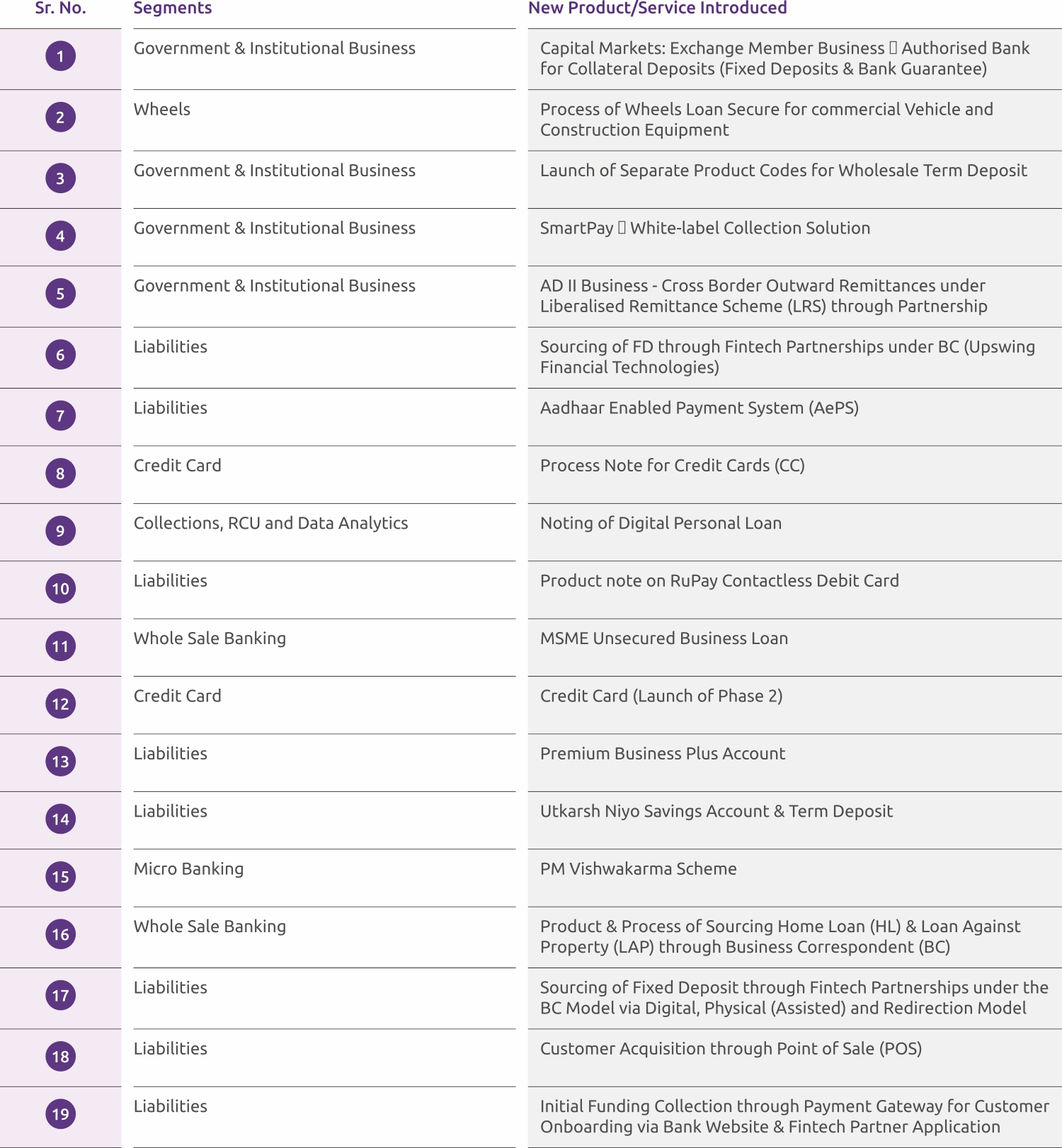
Customer Centricity & Product Innovation
In order to cater to the requirements of all customers, bank introduced total 19 new products/services in segments like MB, Retail Assets, Whole Sale Banking, Gold Loan, Liabilities, Credit Card and Government & Institutional Business. Bank also improved existing 12 products & services to enhance the customer focus. The list of the newly launched products is given below:
- Corporate Governance
- Developing and Managing Risk Management Framework
- ESG Governance & Board Oversight
- Corporate Governance & Business Ethics
- Data Protection & Privacy
- Cybersecurity Governance
- Business Continuity and Disaster Management Plan
- Compliance
Corporate Governance



Developing and Managing Risk Management Framework
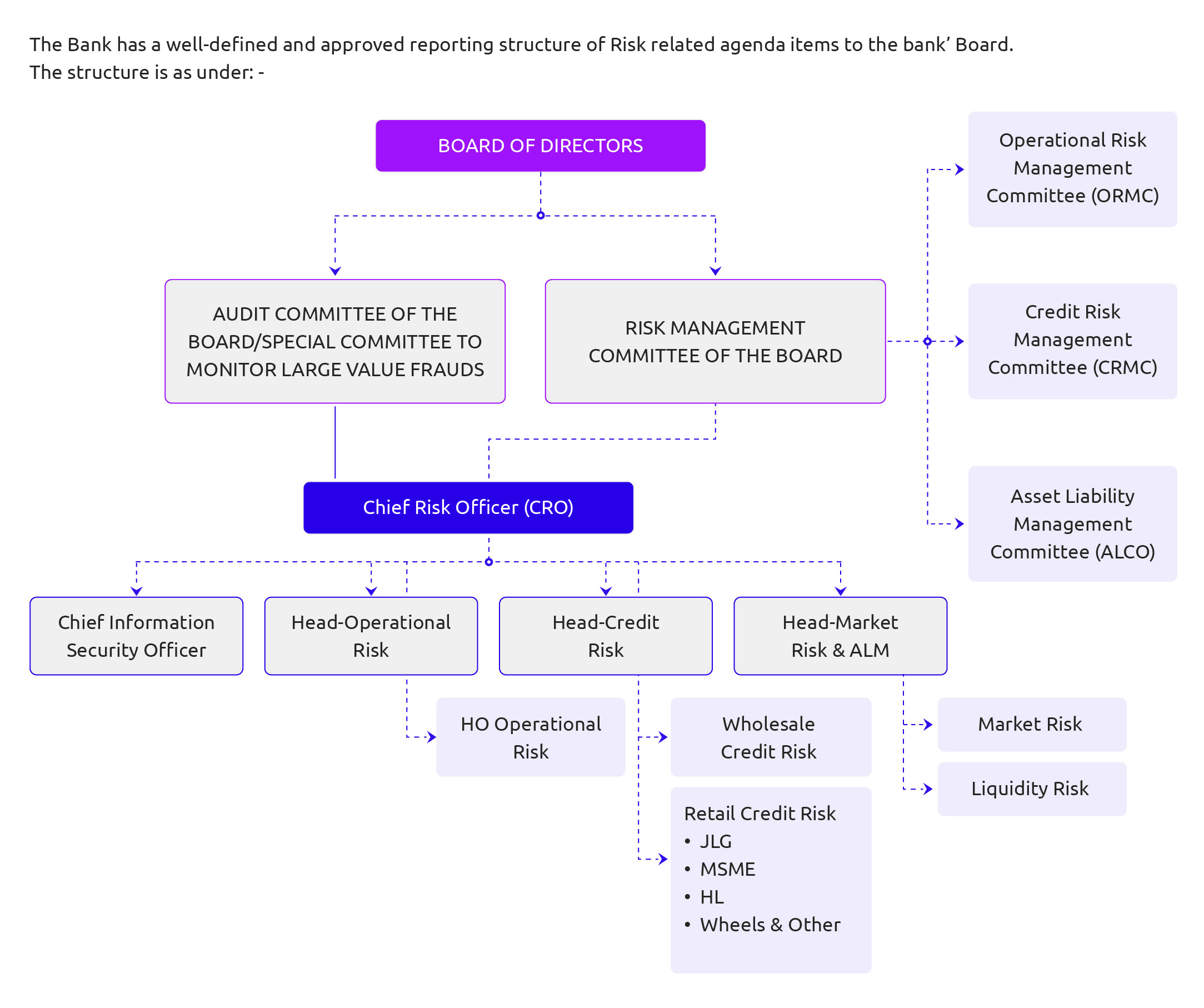
Bank prioritizes robust risk management, focusing on credit assessment and monitoring across various risk categories: credit, market, liquidity, IT, and operational risks. The framework includes real-time monitoring of regulations and market trends, setting risk parameters, defining acceptable portfolio risk, and implementing early warning systems. Utkarsh Small Finance Bank adopts a structured approach, ensuring qualified and experienced officials that lead risk management independently from
business functions. The philosophy aims to safeguard stakeholders’ interests and the bank’s reputation while integrating risk management into growth strategies.
The composition of Risk Management Committee is available in the annual report 2023-24 on page number 48.
Risk Management Policy is available at: https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/pdf/our-policy/template_ten/Risk_Managment_Policy.pdf
ESG Governance & Board Oversight
Bank has created a management level committee having the following constitution. The terms of reference of the ESG committee includes reviewing the ESG performance of the Bank & guide Bank’s future course of actions in terms of ESG including disclosures. ESG Committee is responsible for reviewing and approving the reported information, including the organization’s material topics. The committee should also describe the process for reviewing and approving the information.
ESG Steering Committee
Permanent Members
MD&CEO & Chairman – ESG Steering Committee
Chief Compliance Officer
Chief Risk Officer
Head Credit
(ESG Officer) (Convenor)
Independent External Member (BII)
Permanent Invitees
CFO
CHRO
Head-MB
Head-Assets
Head- Consumer Banking, Liabilities
Policies
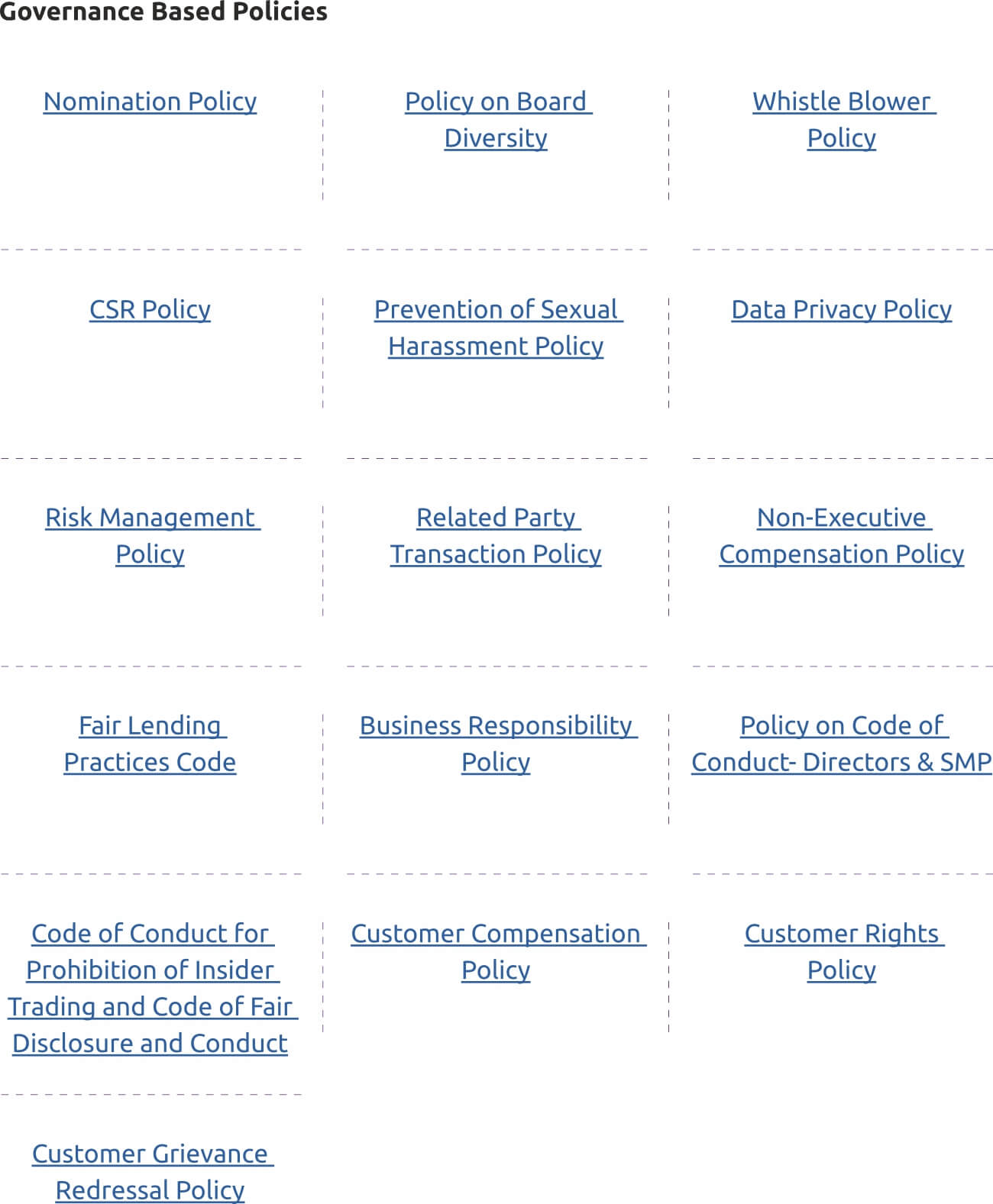
To integrate ESG considerations into all aspects of bank’s operations, Utkarsh has adopted a variety of essential policies, codes of conduct, and guidelines. These measures actively foster and maintain its dedication to responsible banking throughout the organization.
Corporate Governance & Business Ethics
Bank’s Philosophy
Corporate Governance report forming part of the Board’s report for the year under review is attached separately as Annexure A, in the annual report of FY23-24.
Constitution of Board of Directors
The Board of Directors of the Bank are constituted in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 (Act), Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations 2015, the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (the BR Act, 1949) and the Articles of Association. The Board consists of eminent persons with considerable professional expertise in business administration, audit, banking, payment & settlement, compliance, account, finance, human resource, risk, strategy, information technology and other related fields
Committees of the Board of Directors
For effective decision-making, the Board acts through various Committees, which oversee specific operational or strategic matters falling within the ambit of the specific terms of reference of that committee. The Board has constituted 12 such committees. All the Board Committees have a specific charter, and these Committees monitor activities falling within their terms of reference. Additional details of the Board Committees, its composition, attendance, meetings held during the FY 23-24 etc. have been provided separately in Corporate Governance Report.
Conflict of Interest
Bank upholds stringent policies on Code of Conduct for Directors & Senior Management Personnel, accessible on the Bank’s website, providing a framework for addressing norms to avoid conflict of interest situations.
Bank also has Related Party Transaction Policy, which:
Ensures timely identification of the transactions between the Bank and its related parties in compliance with the applicable laws,
Govern the approval process and disclosure requirements to ensure transparency in the conduct of RPT in the best interest of the Bank and its shareholders.
Furthermore, there were no complaints received in relation to issues of Conflict of Interest of the Directors & KPMs in the FY24
Board Evaluation
In accordance with the Companies Act, 2013 (Act) and the framework for Board evaluation, the Nomination and Remuneration Committee and the Board of Directors had carried out, annual performance evaluation of the Board, its Committees and Directors individually. Further, a meeting of Independent Directors was held in accordance with the provisions of the Act.
A questionnaire was prepared for evaluation based on criteria which included providing strategic perspective, attendance, time devoted and preparedness for meeting, quality, quantity and timeliness of flow of information between the members of the Management, contributions at the meetings, effective decision - making ability, role and effectiveness of the Committee. The Directors completed the questionnaire and provided feedback on the functioning of the Board, its Committees and Directors individually and the same noted in the meetings of the Board of Directors. Refer Section 5 for targets related to Board Functioning, Business Ethics & Integrity.

Data Protection & Privacy
Bank is committed to keeping Personally Identifiable Information (PII) secure and using it exclusively for banking-related activities. Bank has implemented a privacy policy designed to protect the personal information provided or disclosed by customers. This policy outlines how the bank collects, uses, discloses, stores, secures, and disposes of personal and sensitive data.
The policy is available on bank’s website:
https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/policy/Data_Privacy_Policy.pdf
The security of personal information is a priority and is protected by maintaining physical, electronic and procedural safeguards that meet applicable laws. The Bank shall take reasonable steps and measures to protect the security
of the customer’s personal information from misuse and loss, un-authorized access, modification or disclosure. The Bank maintains its security systems to ensure that the personal information of the customer is appropriately protected and follows the extant standard protection norms followed for the transmission of information.

Cybersecurity Governance
Bank isISO 27001:2013 certified.
Bank has got the awards from IBA for better Cyber Risk Management consecutively for the past two years (2021-22 & 2022-23).
Cyber Risk Insurance coverage is in place for the bank as a fallback against the risks of cyber incidents.
Bank has Cybersecurity Policy, Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP) and Information Security Policies in place approved by the Board.
Security Operations Centre (SOC) is active on 24x7 basis for real-time monitoring and protection of the bank’s assets.
Cybersecurity Incident Response Team (CSIRT) and Cyber Crisis Management Team (CCMT) are constituted as prescribed under the Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP).
Bank has an independent information security group to manage cyber risks, governed by a board-approved policy. Periodic awareness exercises keep employees updated on security practices. The information security function is driven by both technology and process driven controls. The bank has established effective processes in line with RBI guidelines, ensuring
cybersecurity compliance. Governance and management processes are in place to implement, maintain, and improve policies. Bank meets RBI’s Baseline Cybersecurity Resilience requirements, employing defense-in-depth security measures. Robust Cybersecurity awareness program is in place as part of overall Cybersecurity program for customers, employees, and
partners. Risk Management committee ensures compliance with internal cyber risk policies.
(Risk Management Policy-https://www.utkarsh.bank/uploads/pdf/our-policy/template_ten/Risk_Managment_Policy.pdf)
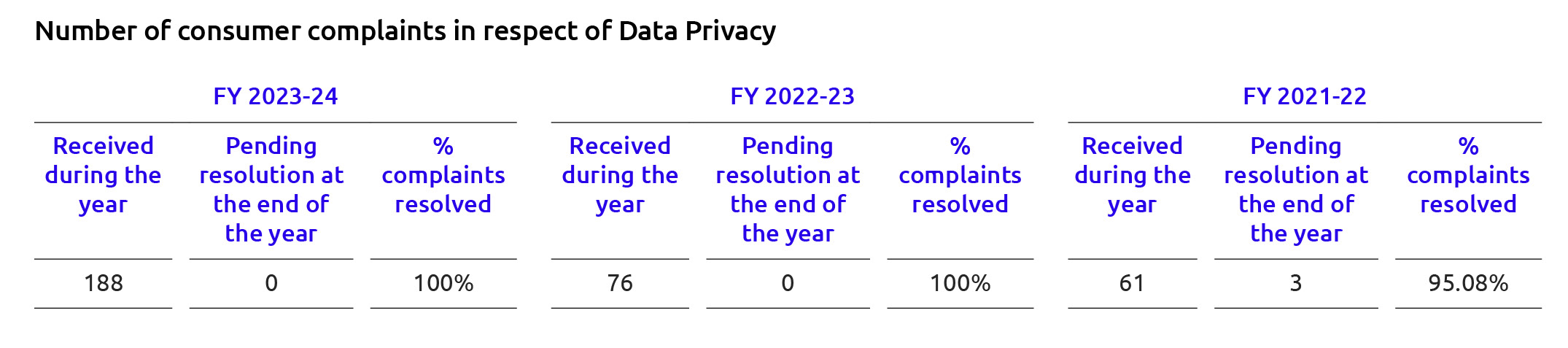
While the number of cyber-security related consumer complaints has been increasing, the efficiency in resolving these complaints has also improved, achieving a 100% resolution rate in the past two years. Utkarsh is positively handling the cyber-security issues, despite the growing volume of complaints
Business Continuity and Disaster Management Plan
Bank has well established Business Continuity Plan (BCP) framework which has been put in place to ensure continuity of service to its large customer base. The effectiveness of the approved Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
framework is tested for all identified critical units to ensure readiness to meet various contingency scenarios and take corrective actions wherever any issues are observed. The Bank has smoothly managed to run its operations
by adapting to various continuity plans. Treasury has put in place robust Business Continuity Plans (BCP) and periodically conducts business from alternate locations as part of BCP

Compliance


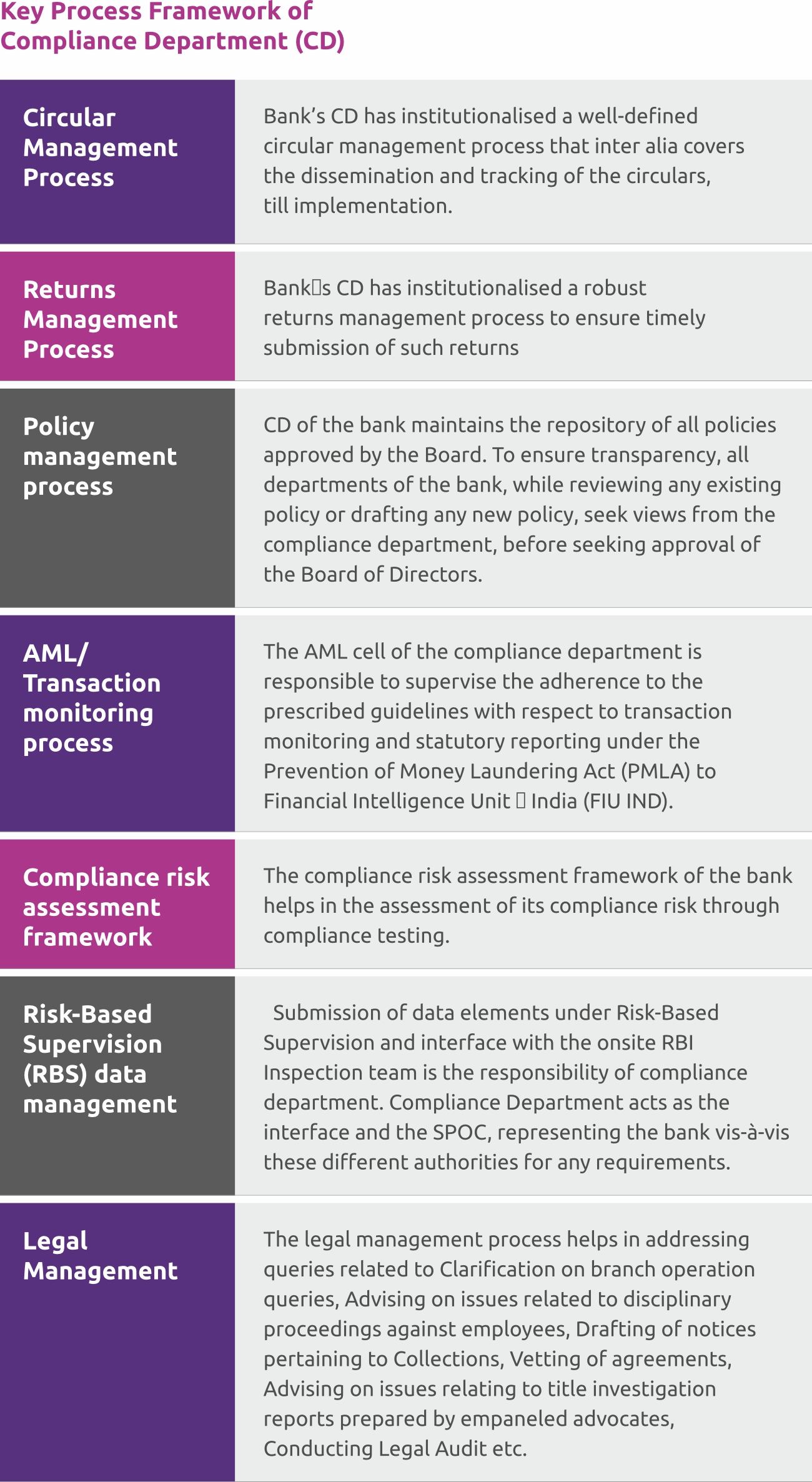
Process framework within the compliance department
Bank’s Compliance Department (CD) consists of Regulatory Compliance, AML Compliance and Legal Compliances. The Compliance Department has an established process of dissemination of guidelines or circulars released by various regulators, review of policies and tracking creation of new policies by the stakeholders, tracking timely submission of returns to regulatory authorities, correspondence with regulatory authorities, transactional alerts monitoring, drafting and vetting of agreements and advising various internal stakeholders on legal Compliances matter. This helps the Bank to ensure effective compliances with policies, regulatory guidelines, and applicable legal framework and action points as per the Regulator’s expectations.
In addition to the interaction with the regulators, the compliance department periodically apprises the bank’s management, Board of Directors, and Board Committees on the changes in the regulatory environment and the status of compliance thereof in the bank. Necessary steps have been initiated towards cultivating and building a strong compliance culture within the bank.
Key Process Framework of Compliance Department (CD)
Tax Compliance
Bank is committed towards maintaining transparency and highest standards of integrity wherein emphasis is placed on the timely and accurate compliance. The tax function is embedded under leadership of Chief Financial Officer. The Board / Audit Committee is periodically kept informed on tax litigations, compliances and updates on tax developments and also tax issues that could have significant impact on organisation. Bank observes compliance with the tax legislation of the country, discharging tax liabilities duly and respects the underlying policy intent
Bank endeavors act in integrity and does not indulge in artificial arrangements to avoid tax through unethical means. Bank observes strong governance practices to abide with the tax principles
Bank adheres to the “maker-checker-reviewer” control mechanism for monitoring the compliance reporting. Bank adheres to the internal SOP’s and the compliance due date calendar / checklist / risk control matrix (RCM) to fulfil the tax compliance. This is further audited by the Internal Audit function on quarterly basis. The grievances raised
elated to tax are addressed within specified TAT and with the collaboration of internal stakeholders. Bank engages with tax consultants for a timely review of reporting requirements and for their opinions on the tax positions of the bank. The same is duly disclosed in the financials and the annual reports. Tax authorities are one of the important stakeholders and we believe in an honest and transparent approach/disclosures in all our submissions. Approach towards managing the tax matters is in line with its corporate purpose, strategy and culture.

ESG Disclosure

Location
You are never too far away from quick banking, check nearest Bank and ATM
Contact
Incase you wish to speak to our banking experts for resolution
Write to us
Whether it be a simple suggestion or feedback or an inquiry.

